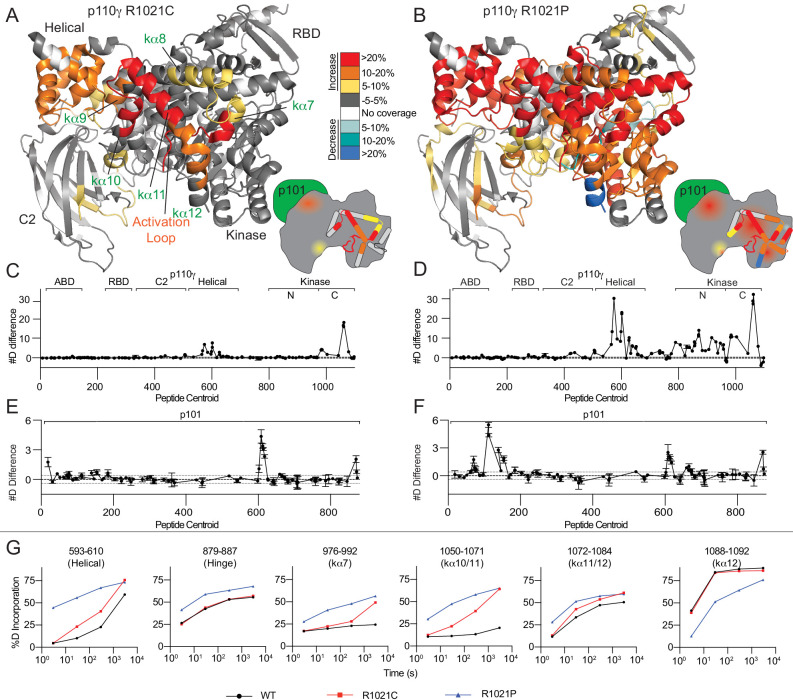
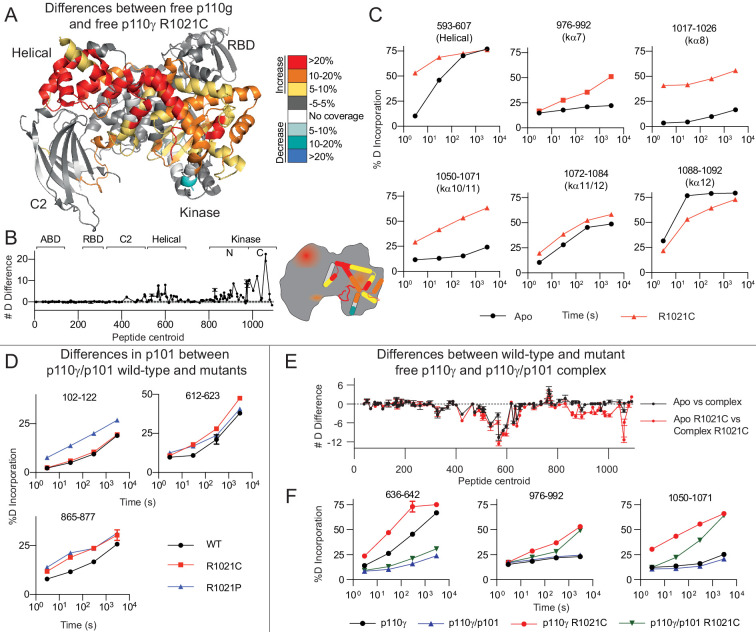
Figure 2. R1021C and R1021P mutations in p110γ are destabilising, with R1021P leading to global destabilisation and R1021C leading to localised disruption of the C-terminal regulatory W1080 Tryptophan ‘lock’.
(A+B) Peptides showing significant deuterium exchange differences (>5%,>0.4 kDa and p<0.01 in an unpaired two-tailed t-test) between wild-type and R1021C (A) and wild-type and R1021P (B) p110γ/p101 complexes are coloured on a model of p110γ (PDB: 6AUD)(Safina et al., 2017). Differences in exchange are coloured according to the legend. (C+D) The number of deuteron difference for the R1021C and R1021P mutants for all peptides analysed over the entire deuterium exchange time course for p110γ. Every point represents the central residue of an individual peptide. The domain location is noted above the primary sequence. A cartoon model of the p110γ structural model is shown according to the legend in panels A+B. Error is shown as standard deviation (n = 3). (E+F) The number of deuteron difference for the R1021C and R1021P mutants for all peptides analysed over the entire deuterium exchange time course for p101. Every point represents the central residue of an individual peptide. Error is shown as standard deviation (n = 3). (G) Selected p110γ peptides that showed decreases and increases in exchange are shown. The HDExaminer output data and the full list of all peptides and their deuterium incorporation is shown in the Figure 2—source data 1 file.