Figure 2.
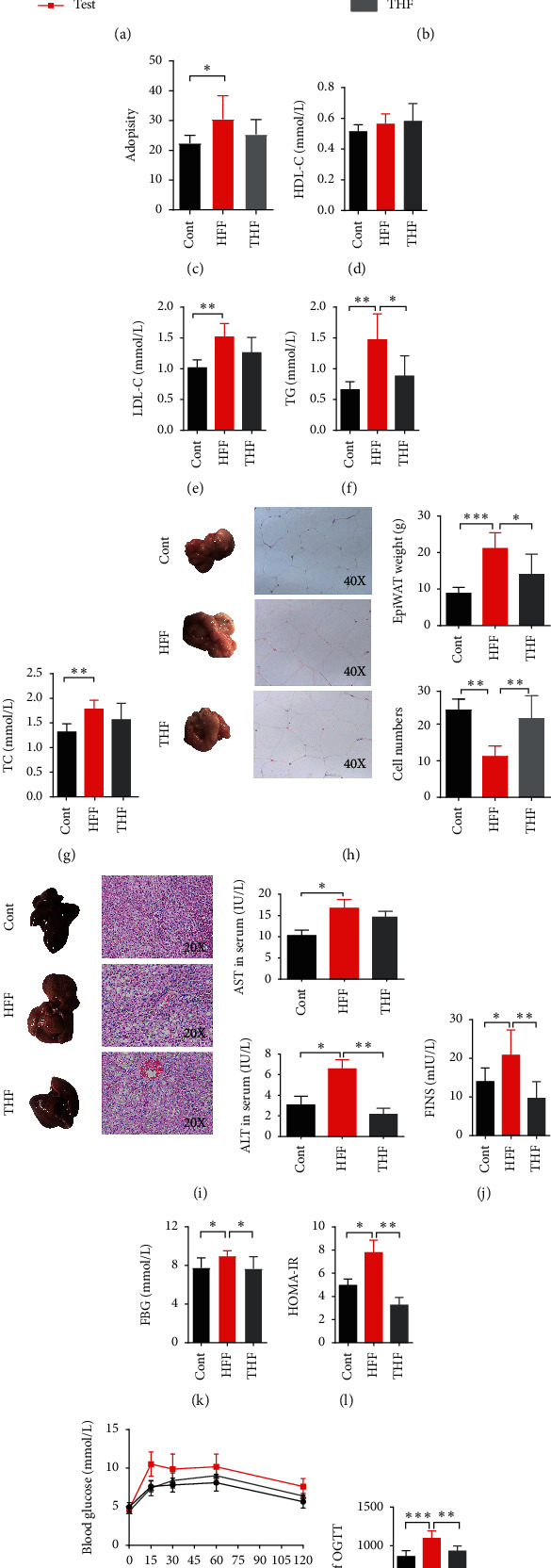
THF improves hepatic steatosis and glucose intolerance of diet induced obese rats. (a) The high-fat high-fructose diet-fed group (test; n = 16) and control group (cont; n = 8) rats were measured for body weight. (b) At the beginning of week 15, the test group rats were divided into HFF-fed and THF (200 mg/kg) treated group (THF; n = 8)) and HFF-fed and vehicle-treated group (HFF; n = 8). The control group, the HFF group, and the THF group rats were also measured for body weight from week 15 to week 19 and (c) adiposity at week 19. Plasma (d) HDL-C, (e) LDL-C, (f) TC, and (g) TG levels were also measured. (h) Representative images of EpiWAT and EpiWAT sections with H&E staining; the EpiWAT weight and cells number were measured; (i) representative images of liver and hepatic tissue sections with H&E staining; serum ALT and AST were also measured; (j) FINS and (k) FBG were measured and (l) HOMA-IR index was calculated; (m) oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT) were carried out, and (n) OGTT-AUC was also calculated. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 6–8); ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001. HFF, high-fat high-fructose diet; THF, Tian-Huang formula, a mixed extract of P. notoginseng and C. chinensis; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglycerides; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; EpiWAT, epididymal white adipose tissue; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; FINS, fasting serum insulin; FBG, fasting blood glucose; HOMA-IR, insulin resistance index.
