Figure 1.
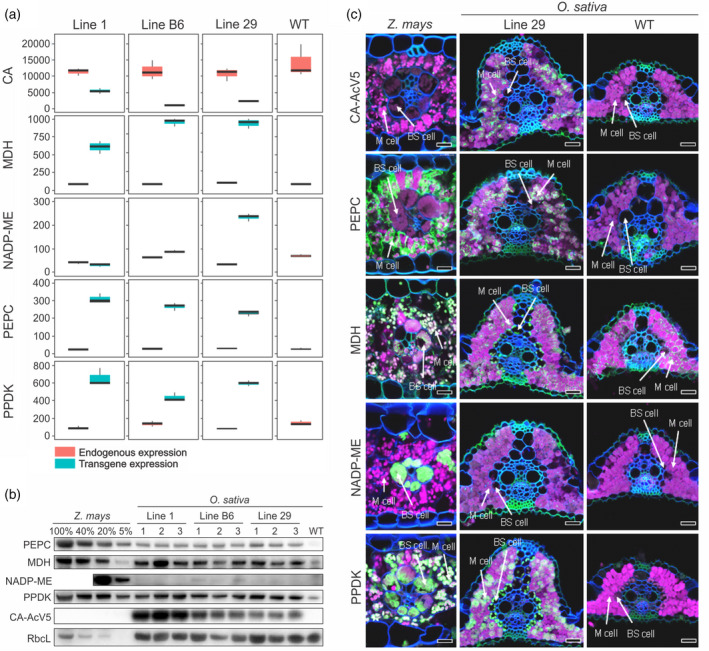
Expression of C4 enzymes in O. sativa. (a) Transcript abundance (in transcripts per million) of Z. mays transgenes and orthologous to them endogenous genes in wild‐type (WT) and three transgenic rice lines. CA, carbonic anhydrase; MDH, NADP‐malate dehydrogenase; NADP‐ME, NADP‐dependent malic enzyme; PEPC, PEP carboxylase; PPDK, pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase. Mean ± SD, n = 3 biological replicates. (b) Immunodetection of proteins in leaf extracts loaded on leaf area basis. Z. mays leaf extract dilution series was used for relative quantification; three plants from each transgenic line were analysed. Signal from RbcL (the large subunit of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase) was used as loading control. (c) Confocal micrographs of protein localization on leaf cross‐sections. Fluorescence signals are pseudo‐coloured: green ‐ protein of interest labelled with secondary antibodies conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488; magenta ‐ chlorophyll autofluorescence; blue ‐ calcofluor white‐stained cell walls. BS, bundle sheath; M, mesophyll. Scale bars = 20 µm. Localization of C4 enzymes in transgenic lines 1 and B6 is presented in Figure S1 and the summary of localization is presented in Table S1.
