Figure 5.
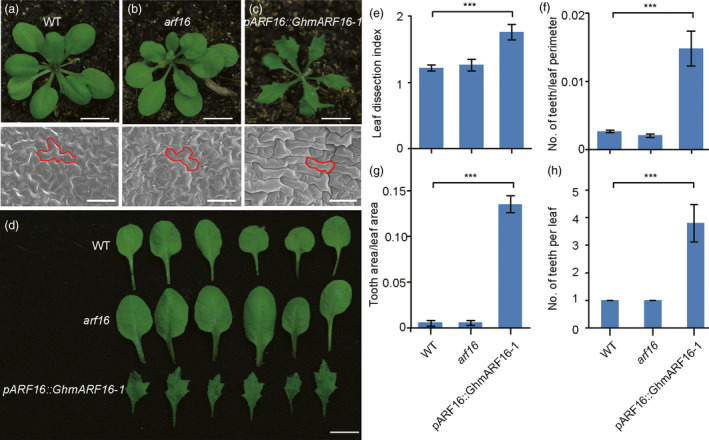
Cotton GhARF16‐1 also functions in modulating leaf shape in Arabidopsis thaliana. (a)–(c) Top, from left to right, 21‐d‐old phenotypes of wild‐type (a), arf16 mutant (b) and pARF16::GhmARF16‐1 transgenic Arabidopsis plants (c). Bars = 4 mm. Bottom, from left to right, scanning electron micrographs of the leaf epidermal cells at the base of the abaxial side of mature leaves of wild‐type, arf16 mutant and pARF16::GhmARF16‐1 transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Bars = 50 µm. (d) Close‐up images of the leaves of 21‐d‐old wild‐type (top), arf16 mutant (middle) and pARF16::GhmARF16‐1 transgenic plants (bottom). (e)–(g) Quantitative comparisons of the leaf shapes of wild‐type, arf16 mutant and pARF16::GhmARF16‐1 transgenic plants based on the leaf dissection index (perimeter2/4π × leaf area) (e), number of teeth/leaf perimeter (f) and tooth area/leaf area (g). (h) Statistical analysis of the number of teeth per leaf from wild‐type, arf16 mutant and pARF16::GhmARF16‐1 transgenic plants. A total of 10 leaves from each line were used for each measurement. Data are presented as mean ± SE. Statistical significance was determined using one‐way analysis of variance combined with Tukey's test. ***P < 0.001. WT, wild type.
