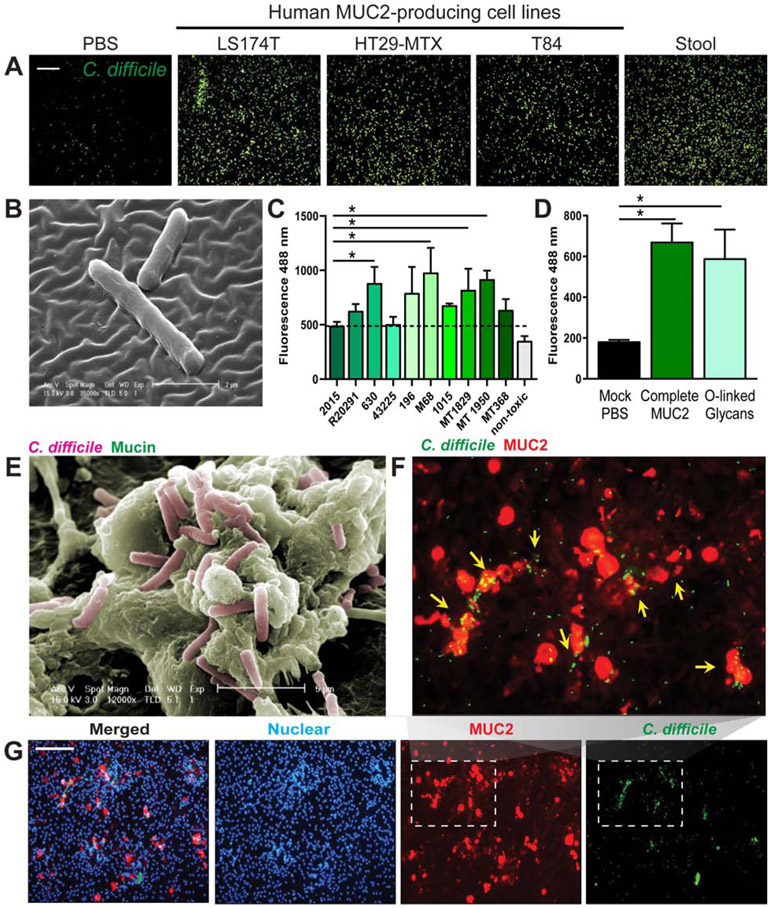
Figure 1: C. difficile adheres to purified human MUC2.
MUC2 was isolated from the supernatants of mucin-producing cell lines LS174T, HT29-MTX and T84, as well as from stool from healthy volunteers by a series of CsCl ultracentrifugation steps. MUC2 (1 mg/mL) was applied to coverslips linked via APTS. C. difficile R20291 was fluorescently-tagged with CFDA-SE and incubated with mucus-coated coverslips for 1 hour. A. Adhesion was visualized by microscopy (scale bar =50 μm) (representative image from n=4 replicates/repeated 3 independent times). B. Scanning electron microscopy of APTS-MUC2 coated coverslips demonstrating adhesion of C. difficile to HT29-MTX-derived MUC2 (representative image; n=3). C. Fluorescently-tagged C. difficile was added to 96-well plates coated with MUC2 purified from HT29-MTX and fluorescence values were obtained using a plate reader (n=8 replicates/repeated 3 independent times). D. Adhesion of C. difficile R20291 to mock (PBS), purified intact MUC2 or isolated MUC2-derived O-linked glycans (n=4 replicates/repeated 2 independent times). E. Co-localization of C. difficile and MUC2 in LS174T cells was also demonstrated by scanning electron microcopy (SEM) (representative image; n=3). F,G. CFDA-SE labeled C. difficile (green) was also found to co-localize with MUC2 (red) positive goblet cells in human colonoid monolayers by immunostaining (scale bar= 100 μM), which is clearly observed in the expanded inset above (F) (n=3 replicates, repeated 2 independent times). ANOVA, *p<0.05.