Figure 5. A VP64-dCas9 fusion protein induces overexpression of Nodal.
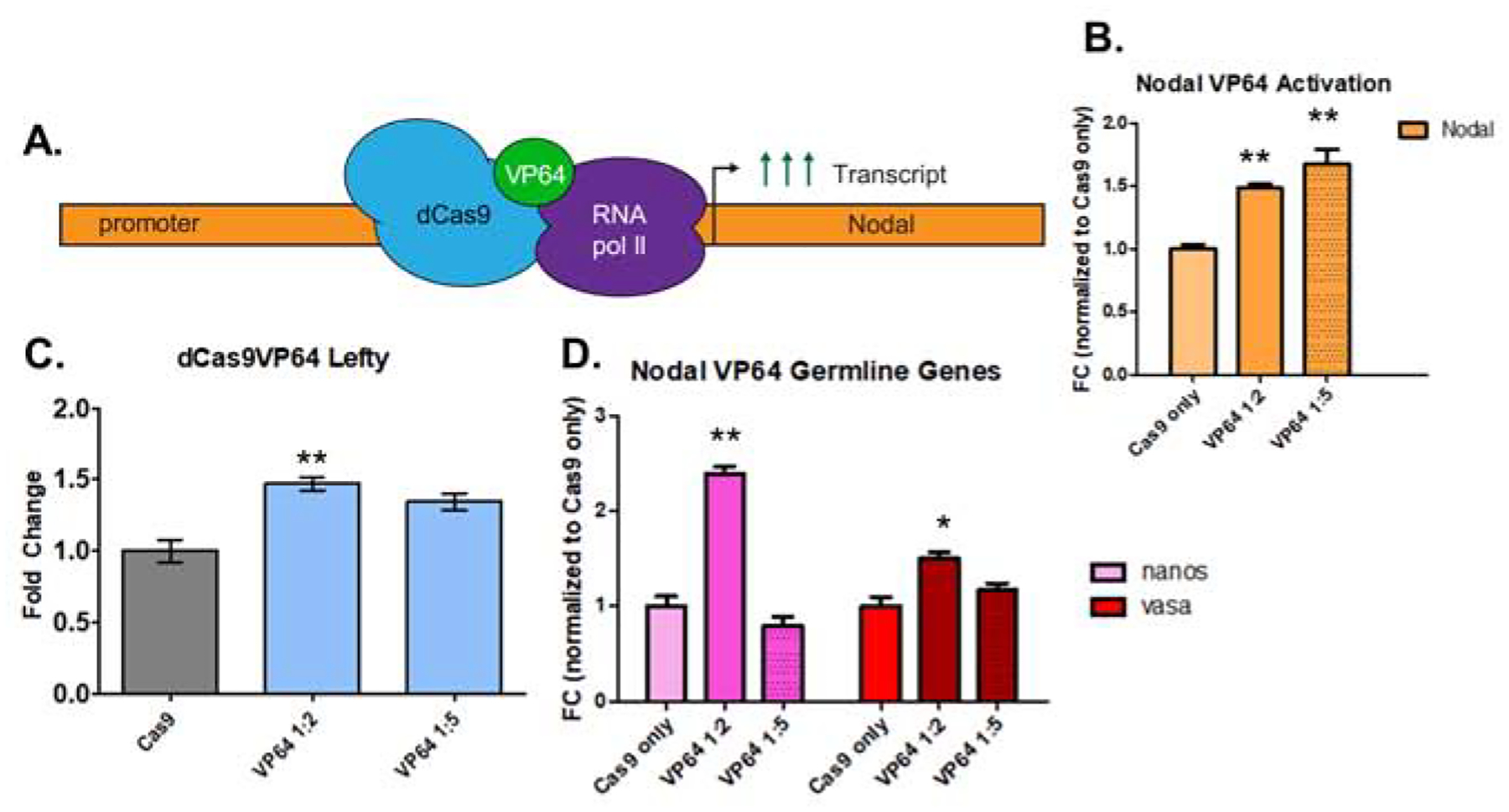
Identifying efficient gRNA targeting in the previous experiments enabled us to test a dCas9-VP64 construct for targeting and activation of Nodal from the defined promoter site. We assessed the effect on Nodal transcription by analyzing the direct downstream target, Lefty, as well as two germline genes: Nanos2 and Vasa.
A. schematic of dCas9-VP64 expression of the Nodal gene. Seven small gRNAs used for the cis-regulatory analysis were used in the overexpression experiment.
B. qPCR analysis of dCas9-VP64 induced nodal overexpression. Two experiments, one in which a 1:2 mass ratio of dCas9-VP64 mRNA to gRNA was used, and another with a 1:5 mass ratio (500ng of Cas9-Vp64 mRNA is used for injection mixes). In both experiments, (n=50 embryos) a statistically significant 1.6-fold upregulation of Nodal relative to Cas9-only injected controls was observed.
C: dCas9-VP64 induced nodal overexpression resulted in an increase of Lefty, a single, direct downstream target of nodal activation in the 1:2 mass ratio injected group.
D. qPCR analysis of the germline genes Nanos2 and Vasa (DDX4) in response to Nodal overexpression. At 18hpf, an increase of the germline genes Vasa and Nanos2 was observed in response to Nodal overexpression.
