Figure 6. Genomic regions upstream of Nanos2 drive ectopic expression of a GFP reporter.
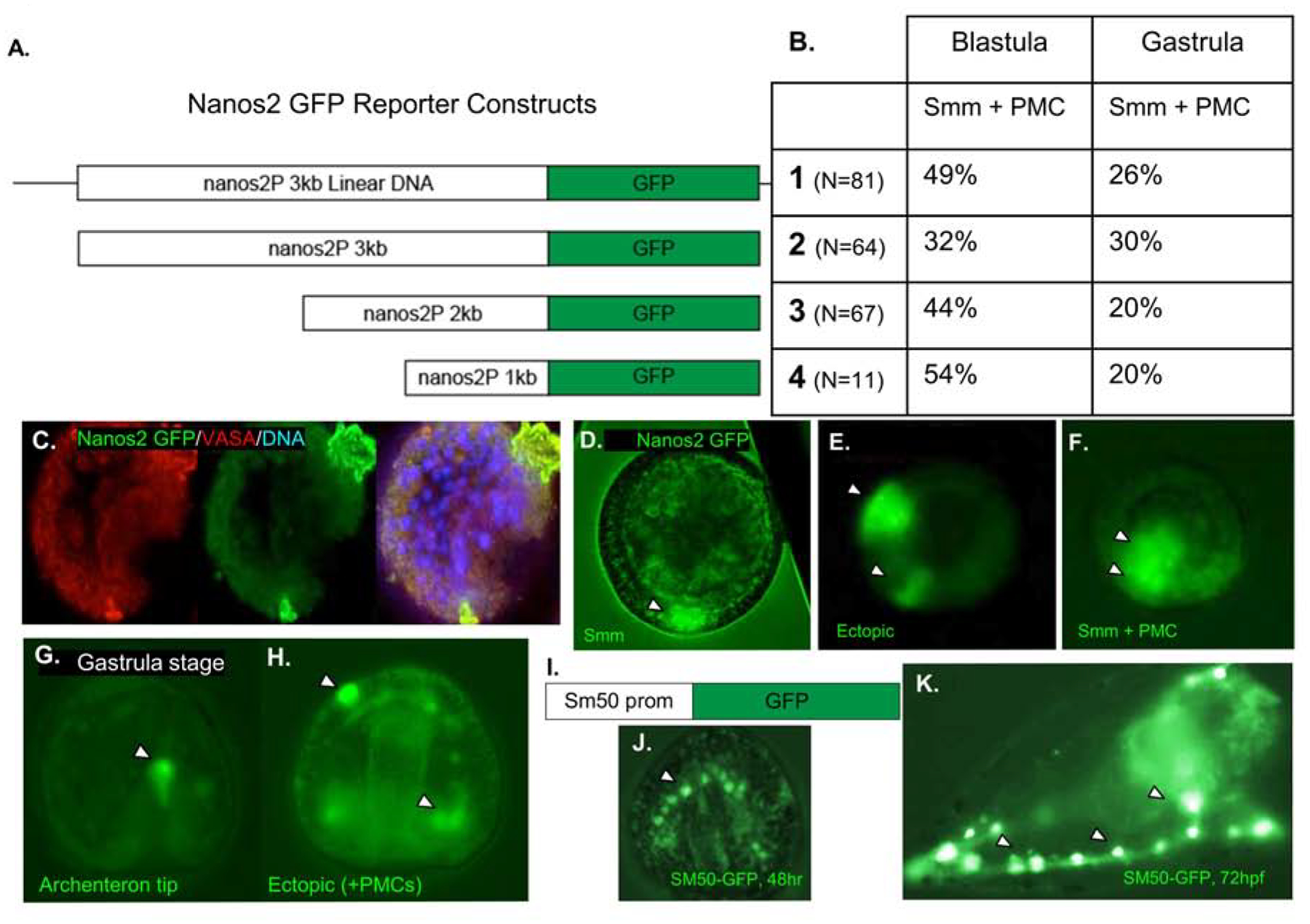
A. Schematic of four Nanos2 promoter GFP fusion constructs that were used in four independent experiments. The first construct is the entire linearized plasmid, while the following three are PCR products from the same construct, producing smaller fragments of the upstream region fused to a GFP reporter.
B. Quantification of Nanos2 promoter GFP reporter expression within the small micromeres (Smms/PGCs) and primary mesenchyme cells (PMCs) as shown in Figure C–H. A negligible number of embryos (<4%, each trial) demonstrated PGC specific GFP localization (shown in C and D). All other embryos demonstrated ectopic expression, and representatives are shown in E–H. No significant difference was seen in expression localization depending on the length of reporter construct injected, and all blastula stage embryos quantified had between 32–54% of embryos with GFP expression localized within PMC + Smms and 40–60% ectopic expression.
C. Representative embryo with Nanos2 promoter driven GFP expression in Smms, counterstained with anti-Vasa antibodies.
D. Representative embryo imaged with Nanos2 promoter driven GFP reporter expressed within the Small micromeres (Smm).
E. 18hpf embryo with GFP expression within the presumptive ectoderm (arrowheads).
F. 18hpf embryo with ectopic GFP expression, in both Smms and PMCs (arrowheads).
G. Representative 48hpf gastrula with GFP reporter in the tip of the archenteron (arrowhead).
H. Representative 48hpf gastrula embryo with Nanos2 promoter driven GFP reporter expressed in multiple different cell types (arrowheads).
I. As a positive control, DNA constructs driving GFP reporter expression by the Sm50 promoter were tested in these experiments
J. At 48hpf, Gastrula stage embryo with GFP expression restricted solely to the PMCs (arrowhead).
K. At 72hpf, Sm50 promoter driven GFP expression is only observed in the PMCs (arrowheads).
