Figure 4. Gut fungi in patients with IBD.
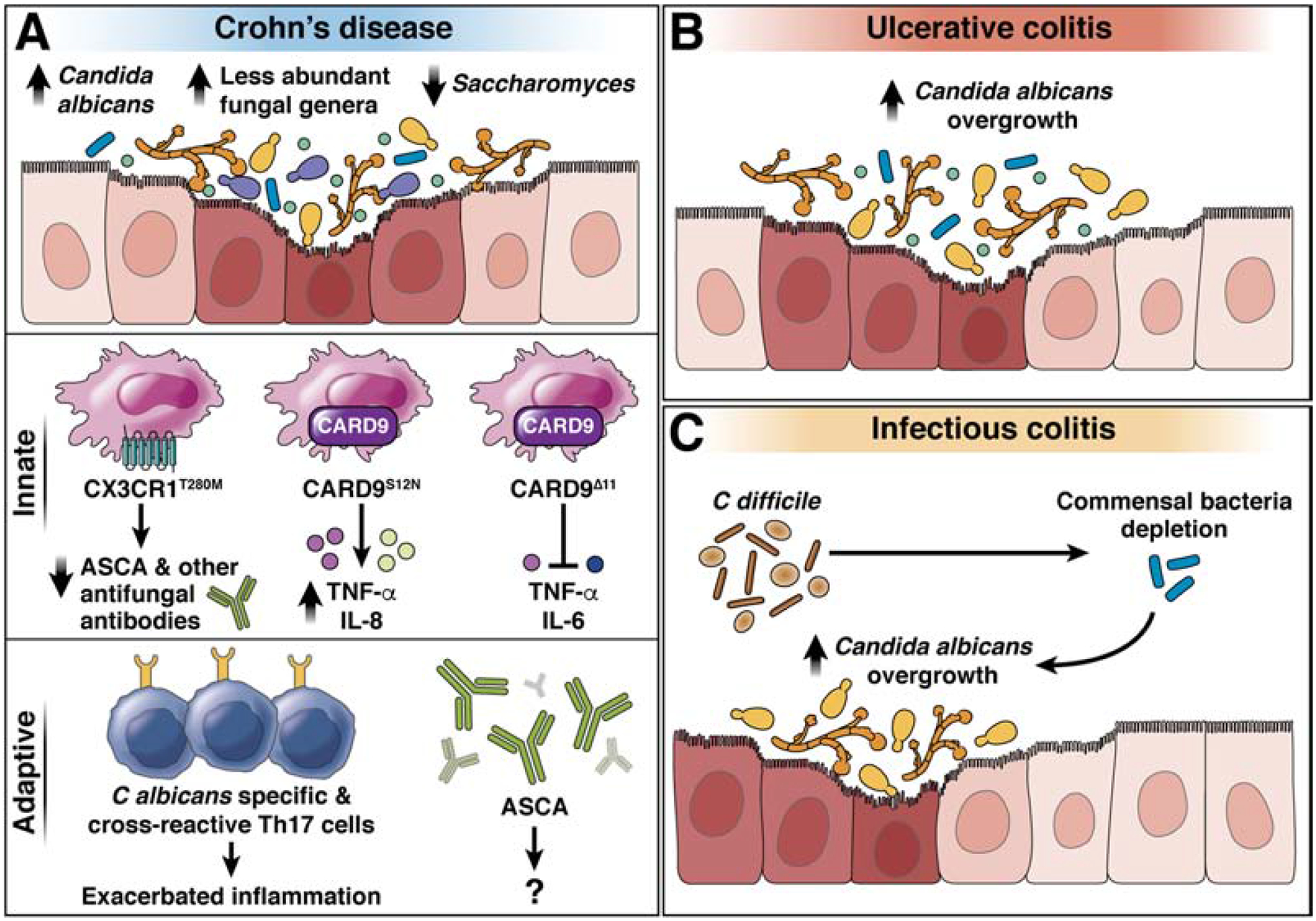
A) Gut fungal dysbiosis, characterized by the overgrowth of opportunistic fungal species, in patients with CD. CD is associated with Candida spp. overgrowth, expansion of less abundant fungal genera such as Malassezia spp., and decrease of Saccharomyces spp. in fecal samples. The T280M mutation in CX3CR1 is associated with decreased ASCA and other antifungal antibodies’ production; the S12N mutation in CARD9 increases production of inflammatory cytokines (TNF, IL8,); the delta 11 deletion in CARD block production of TNF and IL6 to prevent development of CD. Expansion of C albicans-specific and Aspergillus cross-reactive Th17 cells and increase of ASCA antibodies is associated with Crohn’s Disease. Candida albicans overgrowth has been observed in patients with UC (B) and CDI (C).
