Figure 8. Atropine did not affect sEPSCs in GCs of WT and Tg2576 mice.
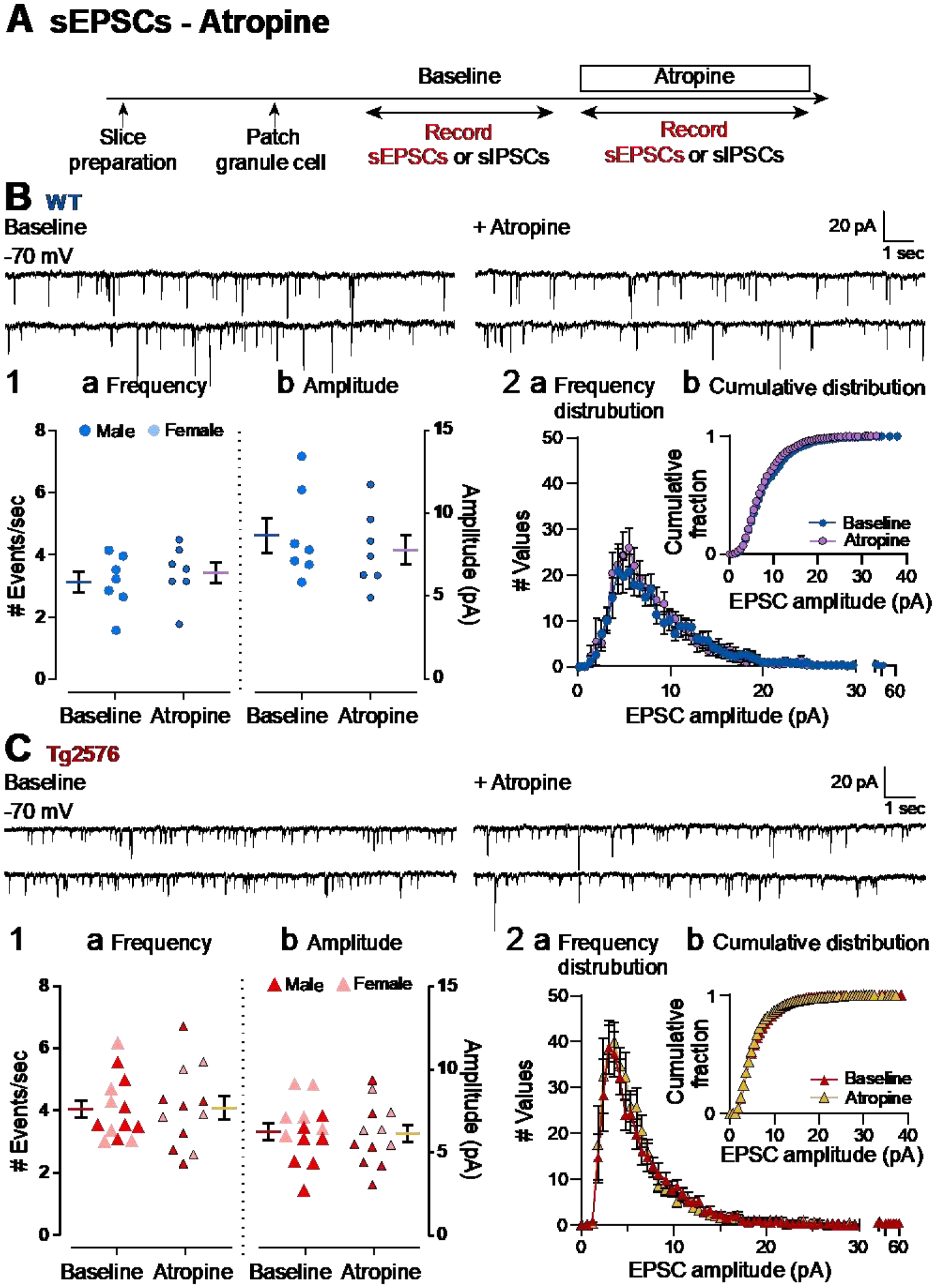
(A) The timeline of the electrophysiological recordings to determine effects of atropine on sEPSCs of WT and Tg2576 GCs.
(B) Representative traces for sEPSCs for WT GCs obtained in baseline conditions (left) and in presence of atropine (right).
(B1) Quantification of the (a) frequency and (b) amplitude of sEPSCs for WT GCs showed no significant effects of atropine.
(B2) Histograms showing the (a) frequency distribution of sEPSCs amplitudes for WT GCs. Insets (b) show that there were no significant effects of atropine on cumulative distributions.
(C) Representative traces for sEPSCs for Tg2576 GCs obtained in baseline conditions (left) and in presence of atropine (right).
(C1) Quantification of the (a) frequency and (b) amplitude of sEPSCs for Tg2576 GCs showed no significant effects of atropine.
(C2) Histograms showing the (a) frequency distribution of sEPSCs amplitudes for Tg2576 GCs. Insets (b) show that there were no significant effects of atropine on cumulative distributions.
