Figure 5. CDN depletes copper efficiently in vivo.
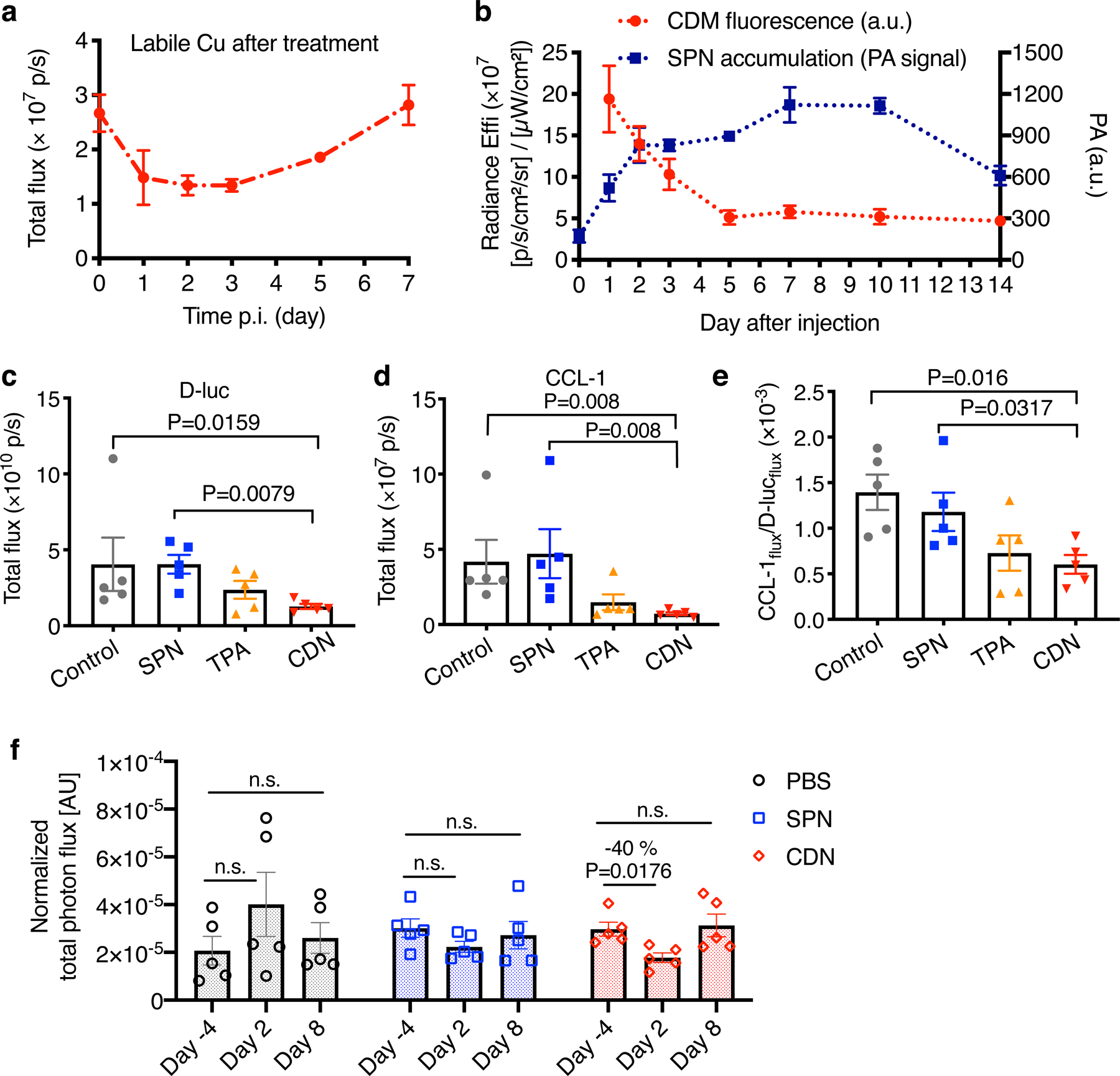
(a) Labile copper concentration detected by CCL-1 bioluminescence imaging after i.v. injection of CDN (1.35 mg/kg) in MDA-MB-231luc tumor bearing mice (mean ± s.e.m., n=3 independent animals). (b) Longitudinal monitoring of nanocomplex delivery and copper binding via optical imaging of CDN after i.v. injection of CDN. Photoacoustic signal in the tumor region (blue) reflects the accumulation and retention of CDN while fluorescence signal reports the copper binding to CDM (red). (mean ± s.d., n=3 independent animals) (c) D-luciferin bioluminescence imaging and (d) CCL-1 imaging of mice receiving SPN, TPA or CDN treatment (chelator dose: 1.35 mg/kg). MDA-MB-231luc tumor bearing mice were i.v. administered with the indicated agents every three days with a total of 5 doses. Images were acquired at day 25 after the first injection (mean ± s.e.m., n=5 independent animals, P value from unpaired t test, two-tailed). (e) The labile copper levels in the tumor region for different treatment groups were quantified as CCL-1 to D-luciferin flux ratio (mean ± s.e.m., n=5 independent animals; P value from unpaired t test, two-tailed). (f) In vivo mitochondrial membrane potential measured by MAL3 bioluminescence imaging. MDA-MB-231luc tumor bearing mice were imaged before and after injection with PBS, SPN or CDN. The total photon flux of MAL3 bioluminescence signals was normalized by D-luciferin bioluminescence signal (mean ± s.e.m., n=5 independent animals, P value from unpaired t test, two-tailed).
