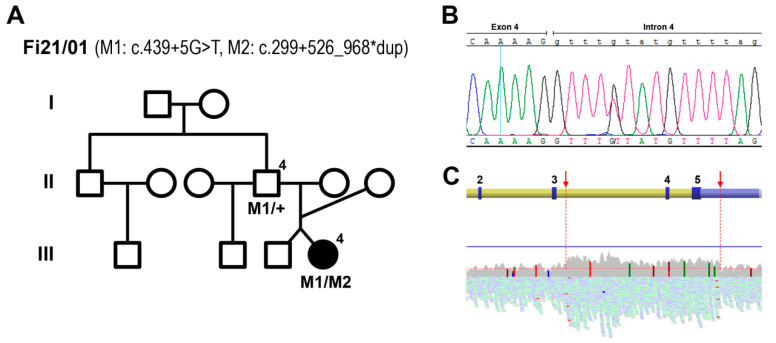
Figure 2.
Genetic screenings allowed the discovery of the molecular cause of disease in the patient. Pedigree from family Fi21/01 (A) show the identified nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase 1 (NMNAT1) pathogenic mutations M1: c.439+5G>T and M2: c.299+526_968*dup. The mutant allelic combination, analyzed by whole exome sequencing, is shown in the patient (individual III.4) and in the father (individual II.4, of Bulgarian origin). The confirmation of M1 was obtained by Sanger sequencing (B). The detection of the genetic rearrangement M2, corresponding to the duplication of exons 4 and 5 of NMNAT1, was detected by analyzing the BAM file from the whole genome sequencing of the patient (C). The upper scheme shows the genetic localization within the gene (exons 2 to 5, numbered), whereas the reading coverage is depicted in the lower graph. The red arrows show the region of the duplication, from the beginning of intron 3 to the middle of the 3′ UTR.