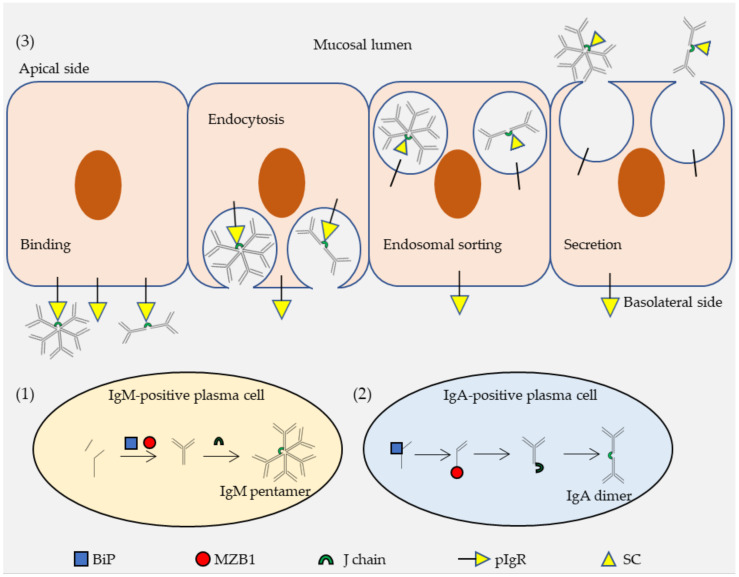
Figure 2.
A proposed scheme for transcytosis of polymerized IgA (immunoglobulin A) and IgM (immunoglobulin M). (1) Formation of the IgM pentamer is mediated by marginal zone B and B-1 cell specific protein (MZB1) and J chain. MZB1 assists the assembly of IgM as a co-chaperone of the glucose-regulated protein 94 (GRP94)-binding immunoglobulin protein (BiP) complex. J chain aids formation of the IgM pentamer. J chain-containing IgM pentamers are secreted from IgM-positive plasma cells. (2) Formation of the IgA dimer is mediated sequentially by BiP, MZB1 and J chain. BiP binds and stabilizes the α heavy chain. MZB1 binds to the α heavy chain and stabilizes the light chain-heavy chain complex. J chain joins two IgA monomers. J chain-containing IgA dimers are secreted from IgA-positive plasma cells. (3) Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (PIgR) mediates transcytosis of IgA dimers and IgM pentamers. IgA dimers and IgM pentamers, via the J chain, bind to the pIgR on the basolateral membrane of the epithelial cells. The Ig-pIgR complex undergoes clathrin-mediated endocytosis and is conveyed through the endosomal sorting pathway. PIgR is cleaved and its extracellular portion, the secretory component (SC), remains bound to the immunoglobulin (Ig) polymers. The SC-Ig polymer complex is released from the apical membrane of epithelial cells and secreted into the mucus. Note that the molecules and cells in this figure are not to scale.