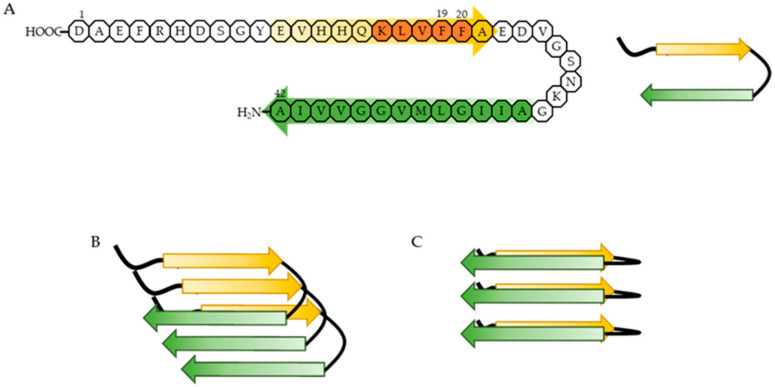
Figure 9.
Proposed mechanism of abnormal Aβ aggregation. (A) Aβ1-42 forms a β-hairpin, including two β-strands. One of the strands is composed of residues 11–24 (yellow arrow) and contains the hydrophobic core domain (orange domain), and the other is composed of residues 30–42 (green arrow), regarded as the hydrophobic C-terminus. The hydrophobic core domain and the hydrophobic C-terminus have hydrophobic interactions. (B) Aβ in its β-hairpin conformation aggregates into soluble Aβ oligomers and forms β-sheets via intermolecular hydrogen bonding. (C) Soluble Aβ oligomers undergo a conformational change into an insoluble form with typical cross- β structure via intermolecular hydrogen bonding.