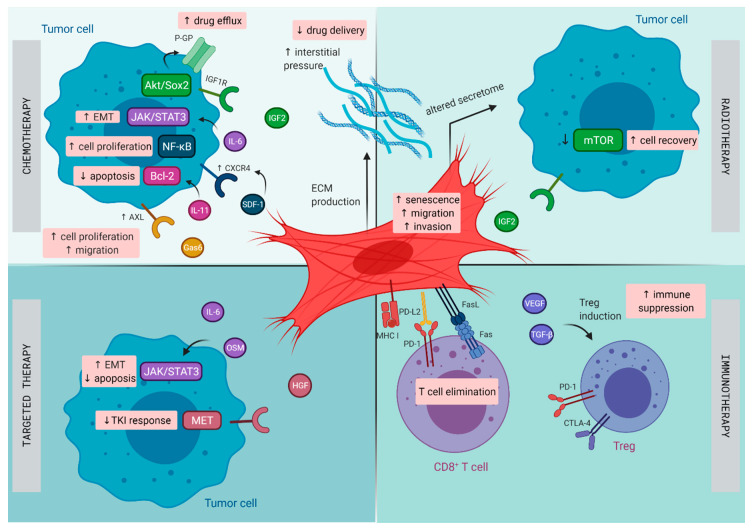
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of therapy resistance in lung cancer orchestrated by cancer -associated fibroblasts (CAFs): Schematic illustration on how CAFs diminish the effect of chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy in lung cancer. CTLA-4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4; CXCR4, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; ECM, extracellular matrix; EMT, epithelial–mesenchymal transition; FasL, Fas ligand; Gas6, growth arrest specific-6 protein; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IGF1R, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; IGF2, insulin-like growth factor 2; IL, interleukin; MHC I, major histocompatibility complex I; OSM, oncostatin-M; PD-1, programmed cell death 1; PD-L2, programmed cell death ligand 2; P-GP, P-glycoprotein; SDF, stromal cell-derived factor; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor; Treg, regulatory T cell; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.