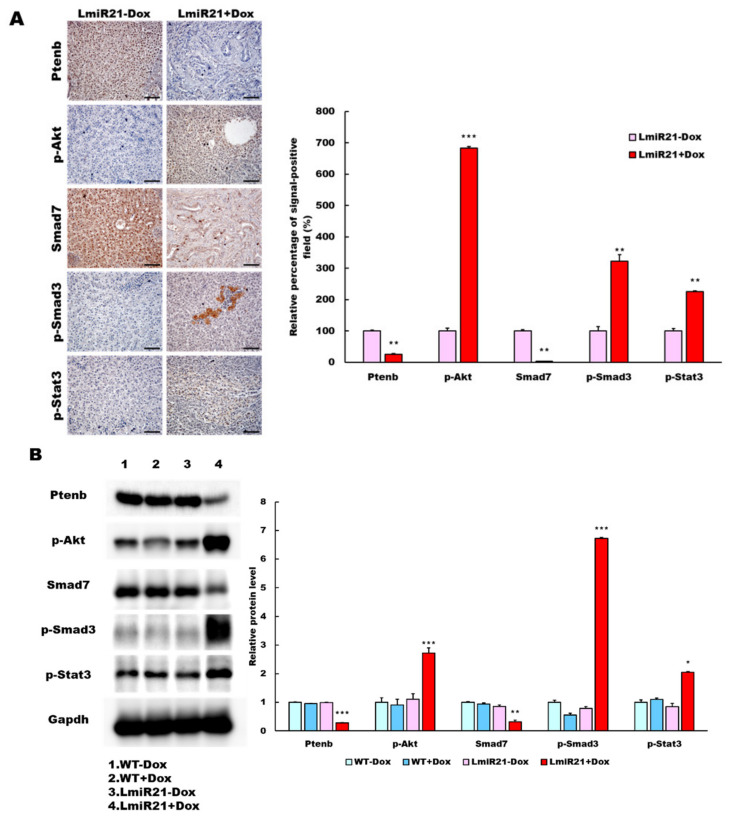
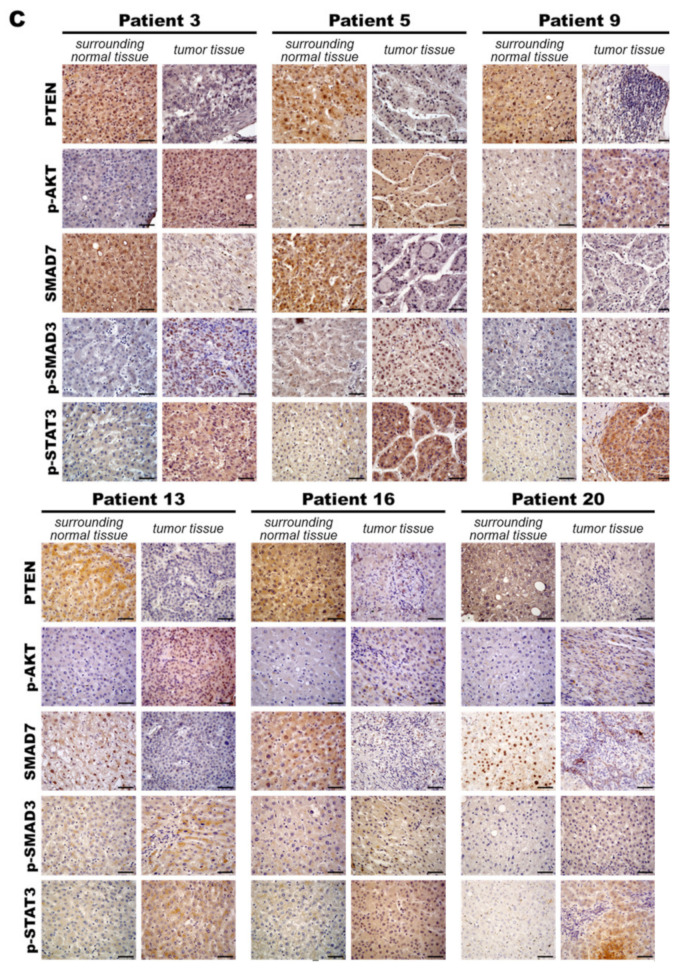
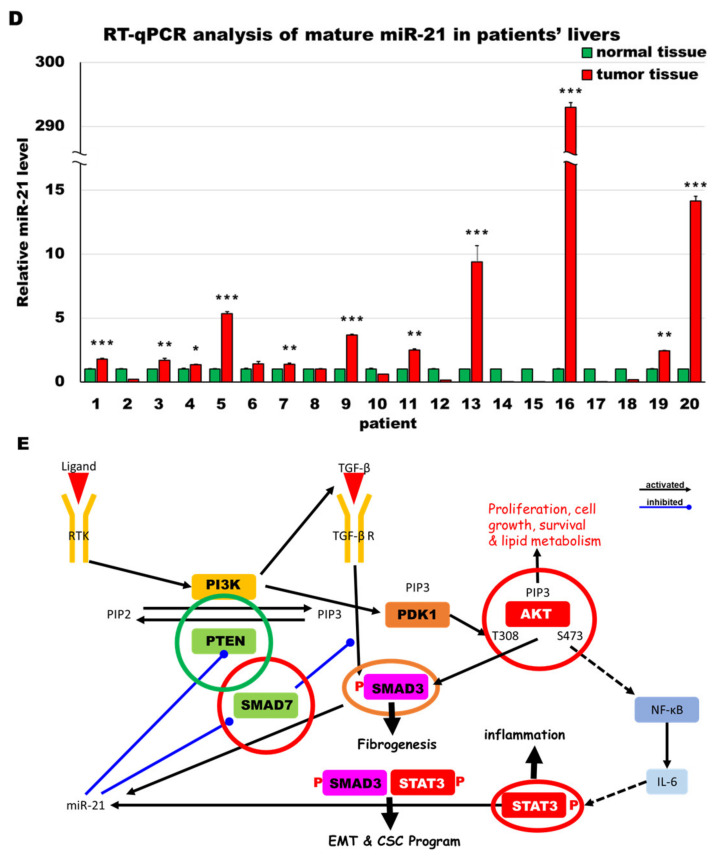
Figure 8.
MiR-21 expression shows a direct correlation with activation of PI3K, TGF-β and STAT3 (PTS) signaling network proteins in LmiR21 zebrafish and human nonviral hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC). (A) Expression patterns of Ptenb, p-Akt, Smad7, p-Smad3 and p-Stat3 in 10 mpf LmiR21 ± Dox liver samples after immunohistochemical (IHC) staining. Scale bar: 50 μm. Positive signal areas per field were quantified. (B) Western blot images (left) and quantitative data (right) of PTS signaling regulatory protein in 10 mpf LmiR21 ± Dox liver. (C) Human nonviral HCC samples (n = 20) were subjected to IHC of PTEN, p-AKT, SMAD7, p-SMAD3 and p-STAT3 expression. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) miR-21 expression profiles in the surrounding normal and liver cancer tissues from nonviral HCC patients (n = 20) were analyzed by RT-qPCR. Positive correlation of miR-21 with PTS signaling regulatory genes in 60% of the nonviral HCC samples were observed. (E) Proposed mechanism by which miR-21 links the NAHCC development. MiR-21 mediates a newly discovered PI3K/Akt, TGF-β/Smad3 and Stat3 (PTS) signaling loop and feed forward loop involving Smad3/Stat3 dependent on miR-21 expression. (Abbreviations: →: activated, ─●: inhibited) Statistically significant differences from LmiR21 − Dox were denoted by * (p < 0.05), ** (p < 0.01) and *** (p < 0.001) for panels A, B and D.