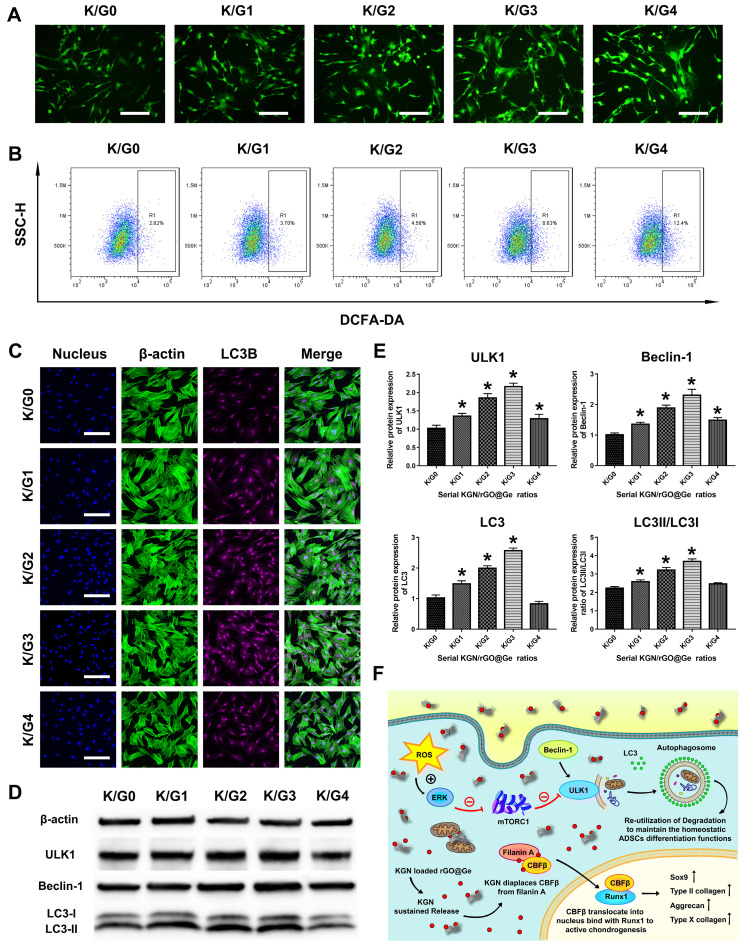
Figure 7.
The change of the autophagy activity in ADSCs cultured with KGN/rGO@Ge medium. (A) The fluorescent microscope images of the intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in the different K/Gs media treated ADSCs, bar: 200 μm. (B) The flow cytometry analysis on the intracellular ROS in the ADSCs treated with the different K/Gs media. R1 gated the quantitative changes of the intracellular ROS in the different groups. (C) The LC3B immunofluorescent staining was used to test the autophagic activities, bar: 200 μm. (D) The Western blot analysis on the autophagic proteins to reflect the autophagy level in ADSCs. The ULK1, Beclin-1, and LC3 were all expressed most in the K/G3 group. (E) The quantitative analysis of the ULK1, Beclin-1, LC3, and LC3II/LC3I. * p < 0.05 indicates a significant difference compared to the K/G0 group. (F) The illustration of the mechanism that KGN/rGO@Ge induced the ADSCs chondrogenic differentiation as the nanocarrier for delivering KGN and regulating autophagy activity. The ROS activated the Erk1/2 signal pathway, then the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) was inhibited and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) within mTORC1 was also inhibited, so the complex of mTOR and ULK1 would disassemble and the dissociated ULK1 from mTOR further initiated the autophagy.