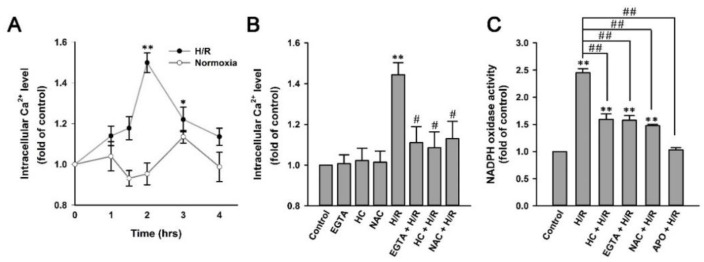
Figure 7.
H/R causes ROS-dependent, TRPA1-mediated increases in intracellular Ca2+ and NADPH oxidase activity in HK-2 cells. (A) HK-2 cells were incubated under normoxia conditions or exposed to 2.5% O2 for 6 h, followed by 1, 1.5, 2, 3, and 4 h of reoxygenation. (B) HK-2 cells were incubated under normoxia conditions as control or exposed to 2.5% O2 for 6 h, followed by 2 h of reoxygenation. In 6 study groups, cells were pretreated with EGTA (an extracellular Ca2+ chelator; 500 µM), HC-030031 (HC, a TRPA1 antagonist; 9 µM) or N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC, a scavenger of ROS; 1 mM). (C) HK-2 cells were incubated under normoxia conditions as control or exposed to 2.5% O2 for 6 h, followed by 2 h of reoxygenation. In 4 study groups, cells were pretreated with HC-030031, EGTA, NAC or apocynin (APO; an inhibitor of NADPH oxidase; 150 µM). Intracellular Ca2+ levels were measured by Fluo-8 fluorescent probe assay. NADPH oxidase activity was measured by NADP+/NADPH assay. Data in each group are mean ± SEM from 5 independent experiments. ** p < 0.01 versus the control group or time zero; # p < 0.05 versus the H/R group without drug pretreatment; ## p < 0.01 versus the H/R group without drug pretreatment.