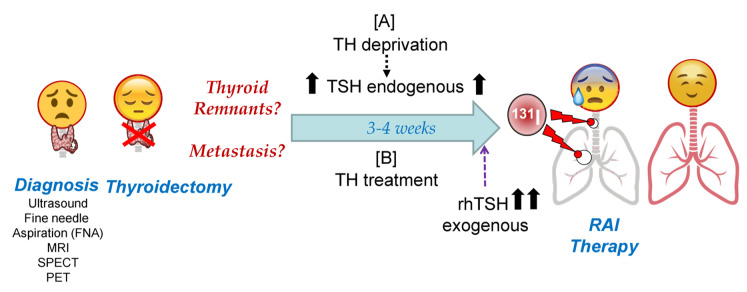
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of Radioactive Iodide (RAI) therapy in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC). After tumor diagnosis, the final goal of both pre-RAI treatments is to achieve maximum radioiodine accumulation in tumor cells, with maximum residence time during 131I therapy. Molecularly speaking, this translates to the maximum accumulation of radioiodine through NIS and the maximum iodine organification in TG or other molecules that are able to oxidize iodide. Abbreviations: TH: Thyroid Hormones; TG: thyroglobulin; TSH: Thyroid Stimulating Hormone; rhTSH: recombinant human TSH; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; SPECT: Single-photon emission computed tomography; PET: Positron emission tomography.