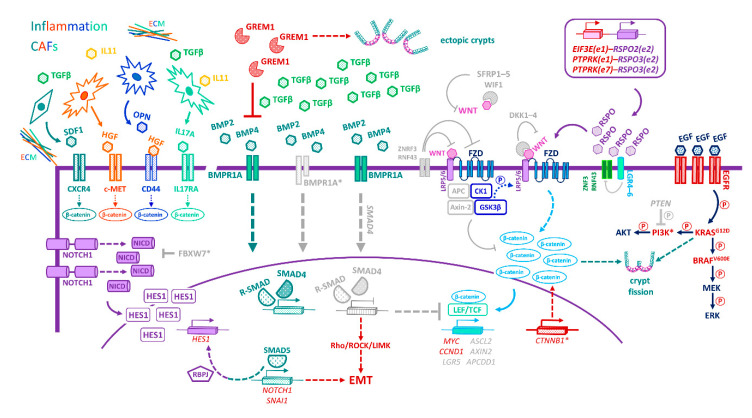
Figure 4.
Mutations in components of niche-signalling pathways lead to “ISC emancipation” and subversion of homeostatic mechanisms. “ISC emancipation”, whereby ISCs gain autonomy from niche signalling, arises when a mutation either negates ISC dependence on pro-proliferative and pro-survival niche signals, or enables ISCs to evade growth-inhibitory stimuli. From right to left: Amplification of EGFR, activating mutations in KRAS (KRASG12D), BRAF (BRAFV600E), or PIK3CA (which encodes PI3K), and PTEN loss-of-function mutations can stimulate MEK/ERK signalling, leading to increased proliferation and survival. The aberrant activation of Wnt signalling during CRC progression is associated with: (1) RSPO2/3 gene fusions that elevate RSPO levels in the TME, (2) epigenetic silencing of genes encoding secreted Wnt antagonists (WNT-ligand antagonists: SFRP1–5 and WIF1; WNT-receptor antagonists: DKK1–4), (3) loss-of-function mutations in negative feedback regulators of the Wnt pathway, such as APC, ZNRF3, RNF43, or Axin2, or (4) activating mutations in CTNNB1 (which encodes β-catenin). The pro-proliferative Wnt-target genes MYC and CCND1 are typically overexpressed, whereas ISC-associated genes are often methylated in aggressive human tumours. Mutations in KRAS or APC correlate with increased crypt fission. Often found in human polyposis syndromes, disruption of BMP gradients (through overexpression of GREM1 or the acquisition of mutations in BMPR1A) leads to the formation of ectopic crypts and polyps. SMAD4 deletion/mutation and/or deregulated TGFβ signalling are further associated with niche independence, EMT, metastasis, and therapy resistance. An inflammatory drive exacerbates tumour progression, with activated CAFs and infiltrating tumour-associated populations elaborating multiple cytokines, including TGFβ, IL11, HGF, OPN, SDF1, and IL17A, which stimulate Wnt/β-catenin signalling and confer aggressive traits. Activation of Notch signalling in advanced tumours is associated with elevated levels of NOTCH1 and HES1, and inactivation of FBXW7, impairing NICD degradation. The Notch and BMP pathways synergize in a SMAD5-dependent manner to induce EMT, and BMPs activate Wnt/β-catenin signalling in the context of SMAD4-deficiency. Grey colouring indicates suppression/inactivation, multiplicity of symbols and/or red denote aberrant upregulation/activation, asterisks signify unspecified mutations, and circled P indicates phosphorylation. Solid arrows indicate direct activation, dashed arrows signify multiple intermediary steps, and lines ending with a bar denote inhibition. CAFs, cancer-associated fibroblasts; ECM, extracellular matrix; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition.