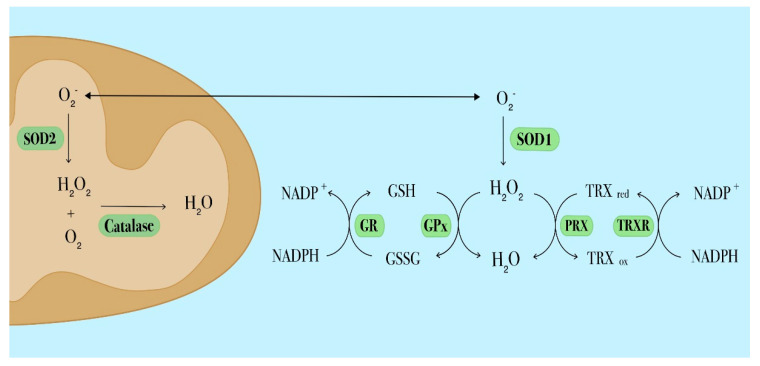
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram depicting the main antioxidant systems in leukemia cells. The superoxide dismutase (SOD) catalyzes the dismutation of superoxide into molecular oxygen and hydrogen peroxide, which is then further processed by catalase. Intracellular SOD isoforms have different locations: SOD1 is located in the cytosol, SOD2 in mitochondria. The glutathione (GSH) antioxidant system comprises GSH, glutathione reductase (GR) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). To perform its antioxidant function, GSH needs to be oxidized into GSSG via GPx. To restore reduced GSH levels, GSSG is converted by GR in a reaction that requires NADPH. The thioredoxin (TRX) antioxidant system involves TRX, peroxiredoxin (PRX) and thioredoxin reductase (TRXR). Reduced TRX catalyzes the reduction of disulfides within PRX. In this process TRX is oxidized (TRXox) and subsequently reduced (TRXred) by thioredoxin reductase (TRXR) through a NADPH-dependent mechanism.