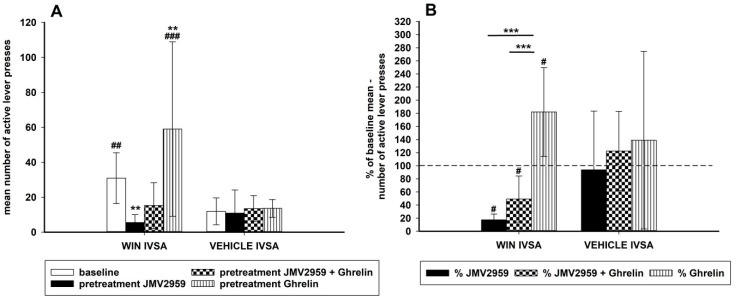
Figure 5.
Additional IVSA experiment: Effects of JMV2959 and ghrelin on active lever-pressing for vehicle and for WIN55,212-2 are illustrated in graph (A). Baseline pressing (mean of three sessions before pretreatment) was influenced by pretreatment with JMV2959 (3 mg/kg) or JMV2959 + ghrelin or ghrelin (40 µg/kg) administered intraperitoneally 20 min before the 120-min sessions. The means of the active lever-pressing are presented as follows: basal lever-pressing (open bar), JMV2959 (filled bar), JMV2959 + ghrelin (dotted bar), ghrelin (striped bar). Differences between WIN55,212-2 IVSA and vehicle IVSA are expressed as ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001. Differences of pretreatments to baseline lever-pressing are expressed as ** p < 0.01. The effects of pretreatments illustrated in the percentage of the average baseline active lever-pressing (graph B) are presented as follows: percentage JMV2959 effect (filled bar), percentage JMV2959 + ghrelin effect (dotted bar), percentage ghrelin effect (striped bar). Differences between WIN55,212-2 IVSA and vehicle IVSA are expressed as # p < 0.05. Differences between pretreatments are expressed as *** p < 0.001. Dotted line shows the baseline active lever-pressing (100%). The additional IVSA data went through logarithmic transformation before the statistical analysis; thus, in the graphs are presented original data together with significances obtained from the transformed ANOVA results. The results are presented as group means with 95% confidence intervals (n = 4).