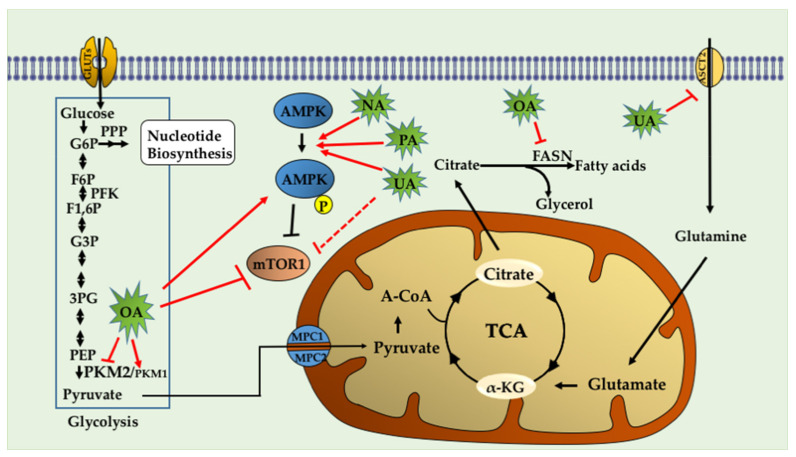
Figure 3.
Triterpenoids target metabolic pathways in prostate cancer. Triterpenoids activate the cellular energy sensor AMPK, promoting catabolic pathways and ATP synthesis, but inhibit the anabolic pathways required for cell growth and proliferation. OA inhibits the enzyme fatty acid synthase (FASN), which catalyzes long-chain fatty acid synthesis. OA also induces expression of PKM1 and reduces expression of PKM2, interfering with the biosynthetic pathways that are sustained by the expression of PKM2 in cancer cells. PCa cells utilize glutamine, which is transformed to glutamate and then to α-ketoglutarate. The latter is shuttled into the TCA cycle. Ursolic acid (UA) inhibits the glutamine transporter ASCT2 and glutamine uptake, and thus the energetic pathways mediated by glutamine. OA: Oleanolic Acid, UA: Ursolic acid, NA: Nummularic acid, PA: Plectranthoic acid, G6P: Glucose-6-phosphate, F6P: Fructose-6-phosphate, F1,6P: Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, PFK: phosphofructokinase, G3P: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, 3-PG: 3-phosphoglycerate, PEP: phosphoenolpyruvate, PPP: pentose phosphate pathway.