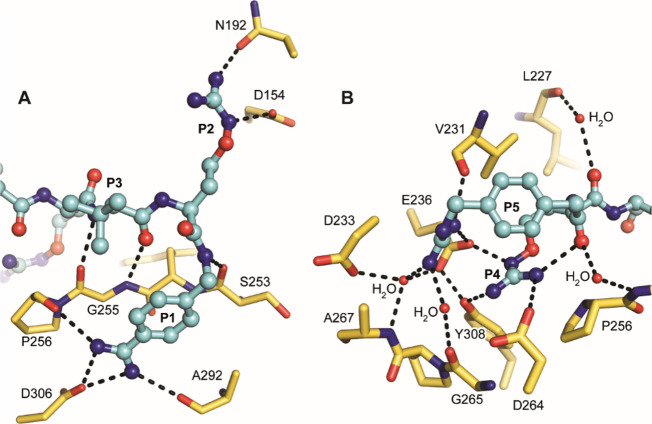
Figure 2.
Polar interactions of inhibitor 8 (ball-and-stick model with carbons in cyan) with furin shown as a stick model with yellow carbons, hydrogen bonds are shown as black dashed lines. (A) Polar interactions of the inhibitor’s P3–P1 segment. The P1 amidine forms a salt bridge to Asp306 and two additional hydrogen bonds with the carbonyl oxygens of Pro256 and Ala292. The P1 backbone NH binds to the carbonyl oxygen of Ser253. The oxyguanidino moiety of the P2 residue interacts with the carboxyl of Asp154 and the side chain of Asn192, respectively. The P3 backbone makes antiparallel beta-sheet-like hydrogen bonds with Gly255. (B) Polar interactions of the inhibitor’s P5–P4 segment. The P4 Cav side chain contacts Asp264, Glu236, and Tyr308, respectively, whereas the P4 carbonyl binds to Leu227 via a water molecule. The P5 guanidino group makes electrostatic interactions with the carboxyl of Glu236 and a hydrogen bond to the carbonyl of Val231. An intramolecular hydrogen bond is formed between the P4 side chain and P5 carbonyl oxygen. Water bridges interactions are found between the P5 carbonyl oxygen and Glu257 NH and from the P5 guanidino group to Gly265, Asp233, and Ala267. It is noteworthy that these interactions of the P5 guanidino group are only observed for conformation A, whereas conformation B is not involved in polar contacts.