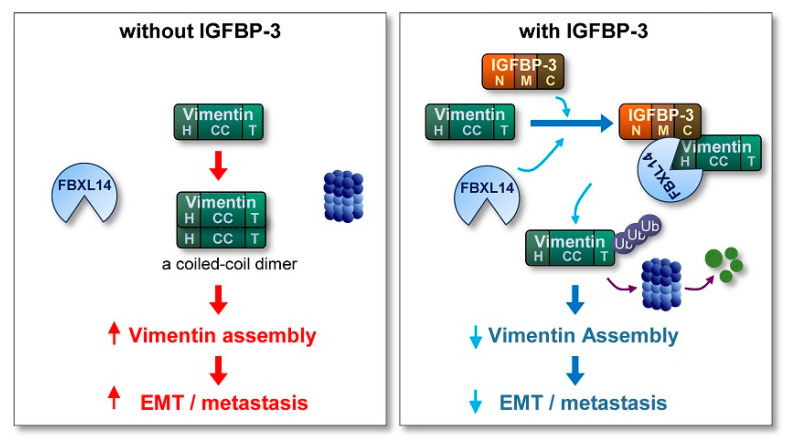
Figure 7.
Schematic model of the mechanism underlying the antimetastatic effect of IGFBP-3. In the absence of IGFBP-3, vimentin protein, which is composed of a central α-helical coiled-coil (CC) domain capped on each side by amino (head; H) and carboxyl (tail; T) domains, forms a coiled-coil dimer, the basic subunit of vimentin assembly, eventually stimulating the EMT program and metastasis of cancer cells. In the presence of IGFBP-3, the vimentin head domain makes a direct interaction with the IGFBP-3 C-terminal domain, resulting in the recruitment of the ubiquitin ligase FBXL14 and proteasomal degradation of vimentin. Consequently, assembled vimentin proteins required for the formation of intermediate filament is reduced, eventually suppressing the EMT program and metastasis.