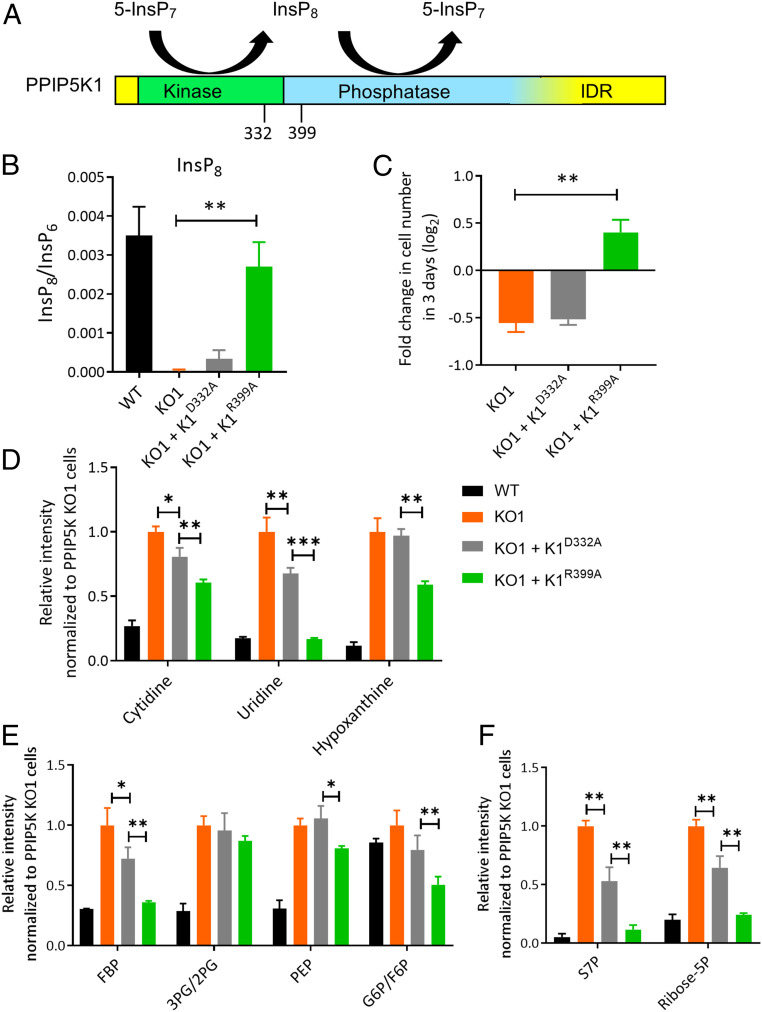
Fig. 4.
The effect of expression of catalytic mutants of PPIP5K1 upon InsP8 levels, cell growth, and selected metabolites in PPIP5K KO cells. (A) Domain structure showing the catalytic bifunctionality of PPIP5K1; IDR = intrinsically disordered region. The blurring of the border between the phosphatase domain and the IDR depicts uncertainty over its location. (B) Cellular InsP8 levels of WT HCT116 cells (black bars), the corresponding PPIP5K KO1 (orange bars), and PPIP5K KO stably expressing either PPIP5K1D332A (gray bars) or PPIP5K1R399A mutants (green bars). (C) Cell growth of PPIP5K KO1 cells and PPIP5K KO1 cells stably expressing either PPIP5K1D332A or PPIP5K1R399A mutants; all cells were cultured in low-glucose medium for 3 d. (D) Relative integrated peak intensities for metabolites in the nucleotide salvage pathway: cytidine, uridine, and hypoxanthine. Here and in subsequent panels, all data are normalized to those obtained from PPIP5K KO1 cells (hence, the latter all have values of 1). (E) Relative integrated peak intensities for glycolysis-related metabolites: FBP, 3PG/2PG, PEP, and G6P/F6P. (F) Relative integrated peak intensities for the phosphate pathway: S7P and ribose-5P. Data for WT cells are calculated from the results in Dataset S1. Student’s t test was used to determine statistical significance of differences between means (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).