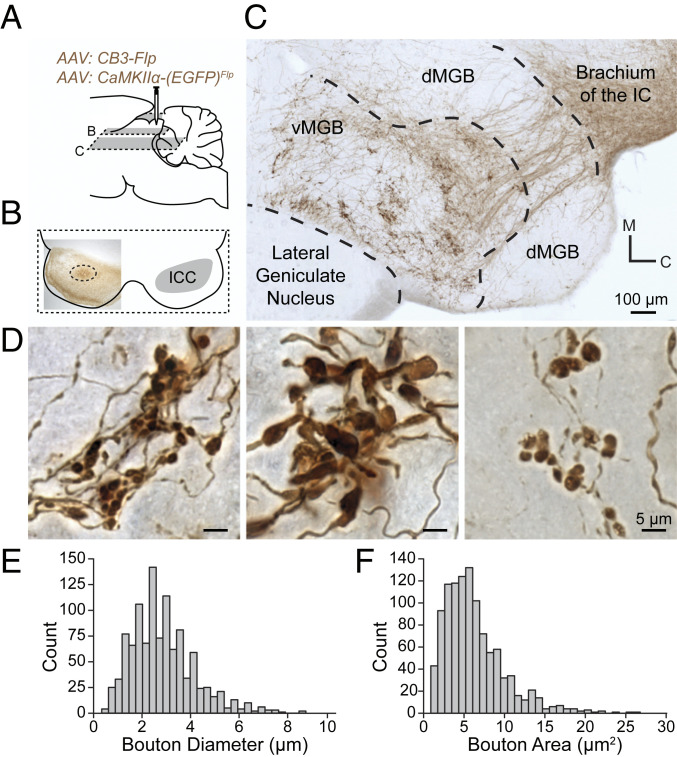
Fig. 2.
CCKE neurons of the ICC have large synaptic terminals in the vMGB. (A) A mixture of two AAVs was stereotaxically injected into the ICC to express EGFP in CCKE neurons. EGFP intensity was enhanced with a biotinylated antibody and visualized with Ni-DAB stain. Gray planes of section denote corresponding locations in B and C. (B) Unilateral ICC injection site (dotted circle) shown in a 65-μm horizontal section. (C) A 65-μm horizontal section from the injection in B. Axons from CCKE neurons travel through the brachium of the IC toward the ventral division of the MGB (vMGB). Groups of terminals cluster in the vMGB. (D) Representative micrographs demonstrating the diversity of terminal morphology in the vMGB from the injection in B. (E and F) Terminal boutons from CCKE neurons in the vMGB were reconstructed. Histograms show the distribution of bouton diameter and bouton area (n = 1,079 boutons, n = 2 gerbils).