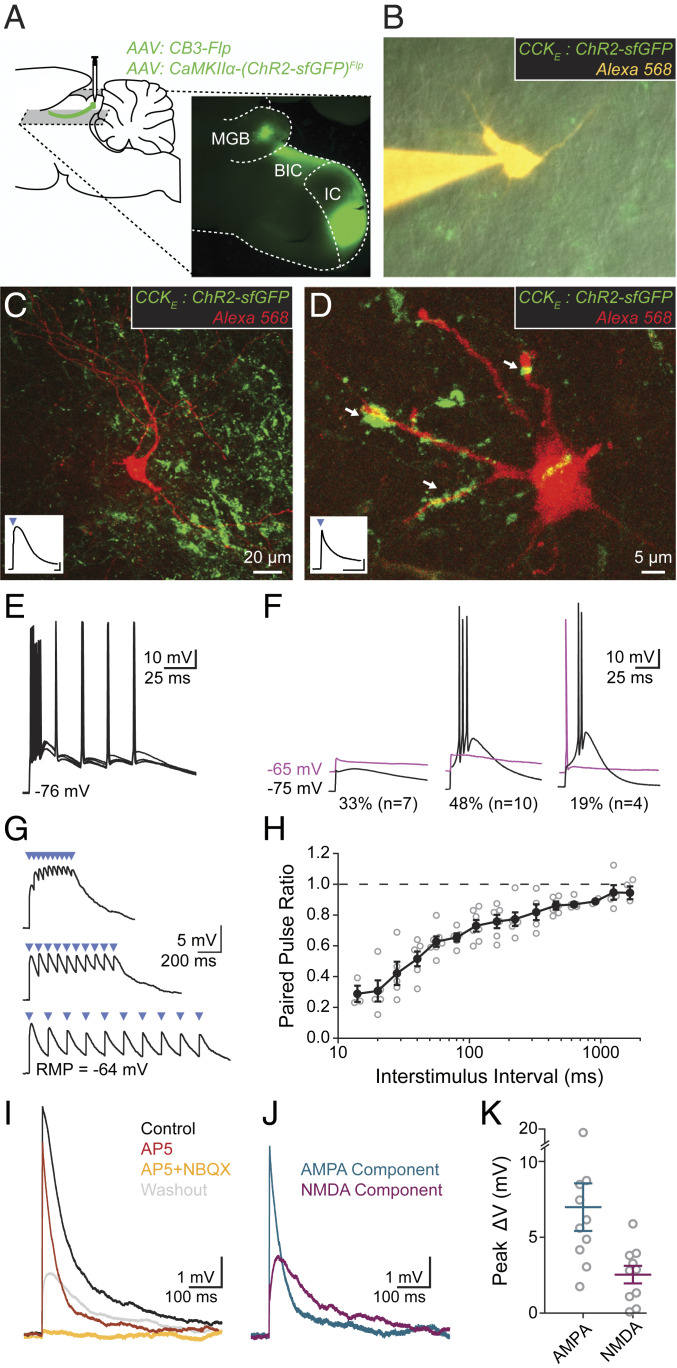
Fig. 3.
CCKE inputs to vMGB neurons mediate large responses through ionotropic synapses exhibiting short-term depression. (A) AAV was unilaterally injected into the ICC. Horizontal slices (200 to 250 μm thick) containing the IC and MGB were made for slice physiology experiments. (B) vMGB neurons surrounded by axons from CCKE neurons (green) were targeted for whole-cell patch-clamp recordings and filled with an Alexa dye (orange). (C and D) Confocal images of recorded vMGB neurons. Insets show light-activated EPSPs (2-ms blue light pulse, blue triangle) in the vMGB neuron. EPSP in C exhibits widening through activation of low-voltage-activated calcium channels. Axons surrounding neurons with confirmed connections showed diverse terminal sizes and shapes. Arrows in D highlight a diversity of putative-synapse sizes. (Inset trace scale bars: 1 mV, 20 ms.) (E) Light stimulation of CCKE fibers evoked spikes in 67% (n = 14/21) of vMGB neurons. Spikes were reliable at stimulation rates exceeding 50 Hz. (F) 33% of neurons (n = 7/21) had subthreshold light-evoked EPSPs at both hyperpolarized (−75 mV, black) and depolarized (−65 mV, magenta) holding potentials. A total of 48% of neurons (n = 10/21) had light-evoked spikes at hyperpolarized potentials and subthreshold EPSPs at depolarized potentials. The remaining 19% of neurons (n = 4/21) had light-evoked spikes at both hyperpolarized and depolarized holding potentials. (G) Trains of light-evoked (blue triangles) CCKE inputs to vMGB neurons show short-term depression and temporal summation. (H) Paired-pulse ratio is plotted as a function of interstimulus interval for vMGB neurons that received light-evoked EPSPs from CCKE neurons. Closed circles and error bars are mean ± SEM. Open circles correspond to individual neurons. n = 7 neurons, n = 6 gerbils. (I) AMPA and NMDA components of EPSPs from CCKE neurons were pharmacologically isolated using sequential addition of 50 μM D-AP5 (red) and 50 μM D-AP5 + 15 μM NBQX (orange). The D-AP5 + NBQX condition fully blocked all responses. EPSPs were recovered after drug washout (gray). n = 10 neurons, n = 9 gerbils. (J) Relative amplitudes of the AMPA and NMDA components were calculated from the subtraction of control and drug conditions. AMPA component (blue): control D-AP5 conditions; NMDA component (magenta): D-AP5–D-AP5/NBQX conditions. (K) EPSPs from CCKE neurons have large AMPA (7.00 ± 1.59 mV) and NMDA (2.49 ± 0.59 mV) components. Peak voltages were measured from calculated AMPA and NMDA components.