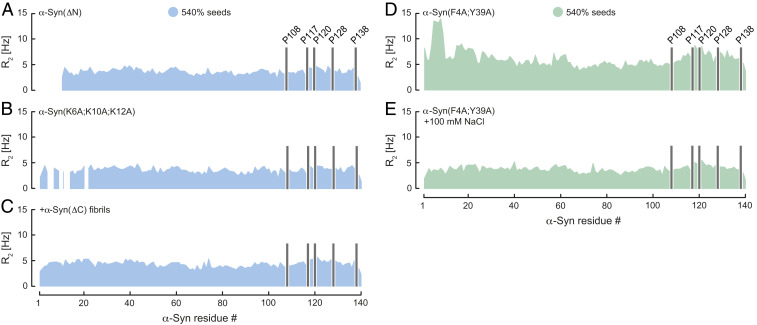
Fig. 2.
Transient α-Syn mutant monomer–fibril interaction. Residue-resolved 15N R2 relaxation rates of (A) α-Syn(ΔN), (B) α-Syn(K6A;K10A;K12A), and (C) α-Syn in presence of wild-type α-Syn and α-Syn(ΔC) fibrils at pH 7. R2 of α-Syn(F4A;Y39A) upon addition of wild-type α-Syn fibril seeds in the (D) absence and (E) presence of 100 mM NaCl at pH 6. Seed concentration is expressed as percentage of soluble α-Syn concentration. Positions of C-terminal α-Syn proline residues without peptide amide resonances are shown in one-letter amino acid code.