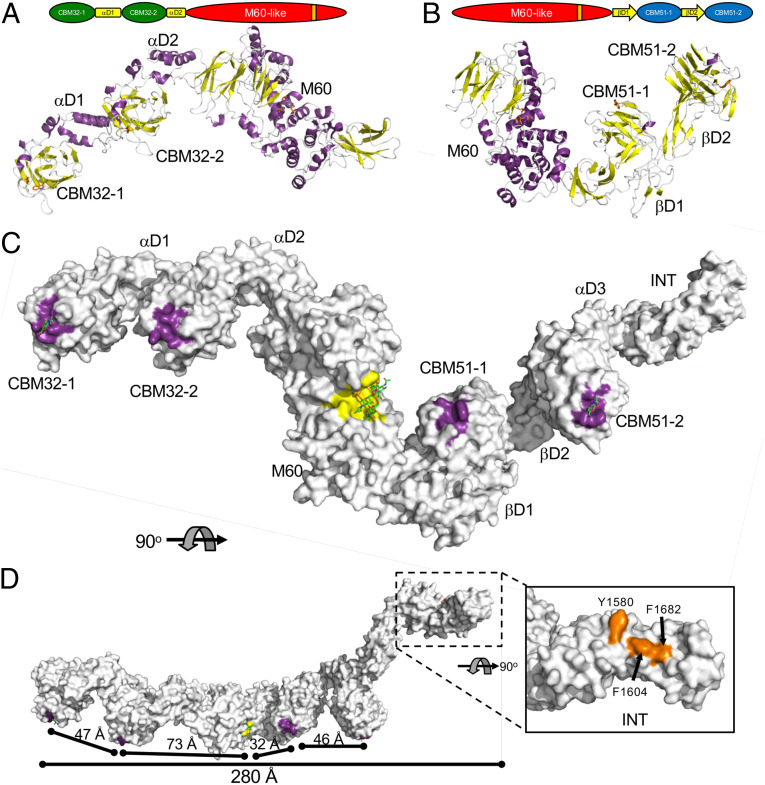
Fig. 5.
Structure full-length ZmpB. Cartoon representations of the 4.6 Å crystal structures of (A) CBM32/M60 and (B) M60/CBM51. Modular schematics of the crystallized and modeled protein according to Fig. 1 are shown for each protein. (C) The full-length composite structure of ZmpB. The CBM32/M60 and M60/CBM51 were overlapped via their M60 domains, resulting in a model of CBM32/CBM51. The CBM51-2 module of this intermediate structure was overlapped with the CBM52-2 module of the βD2/INT structure to generate an initial full-length model of ZmpB. Finally, where possible, the modules/domains were replaced with the high-resolution structures of relevant complexes to generate the final full-length model, which is shown as a solvent-accessible surface. The complex of the M60 domain with an α-2,6-sialylated core 3 pentapeptide (PDB ID 5KDS) was used for this domain (5). D shows an alternate orientation of ZmpB rotated by 90°. In C and D, the surfaces contributing to known or putative carbohydrate binding sites are colored purple. The glycopeptidase active site is shown as a yellow surface. The inset in D shows the distinctive apolar solvent-exposed surface in the INT domain as orange. GalNAc in the CBM32-1 and GlcNAc in the CBM51-2 binding sites are shown as green sticks. The α-2,6-sialylated core 3 pentapeptide is shown in the glycopeptidase active site as green and orange sticks (only the glycosylated threonine of the pentapeptide is shown). Relevant dimensions are indicated. In all panels, the modules/domains are labeled according to Fig. 1.