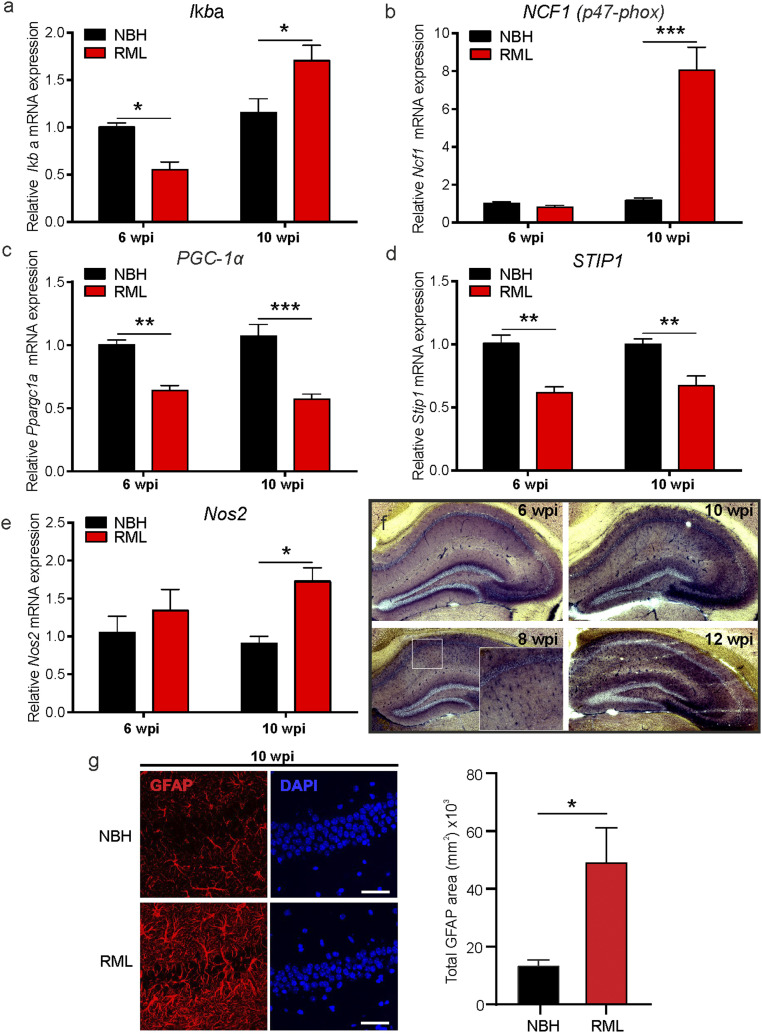
Fig. 1.
Neuroinflammation is enhanced early in prion disease. mRNA levels were determined at 6 and 10 w.p.i. in control (NBH) and prion-infected (RML) mice for the following genes: (A) Iκbα, (B) NCF1, (C) PGC-1α, (D) STIP1, and (E) Nos2. (F) NADPH diaphorase staining of prion-inoculated brains (RML) at 6 to 12 w.p.i. shows enhanced signals in disease detectable after 6 w.p.i. with strong signals in the CA1 and at later time points spreading across the whole hippocampus. (G) (Left) Immunocytochemistry images show representative GFAP and DAPI staining in the hippocampus of NBH and RML mice at 10 w.p.i. and (Right) GFAP signals presented as absolute area. (Scale bar: 50 μm.) Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 4 NBH and n = 7 RML mice, two-way ANOVA (A–E) and unpaired Student’s t test (G), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.