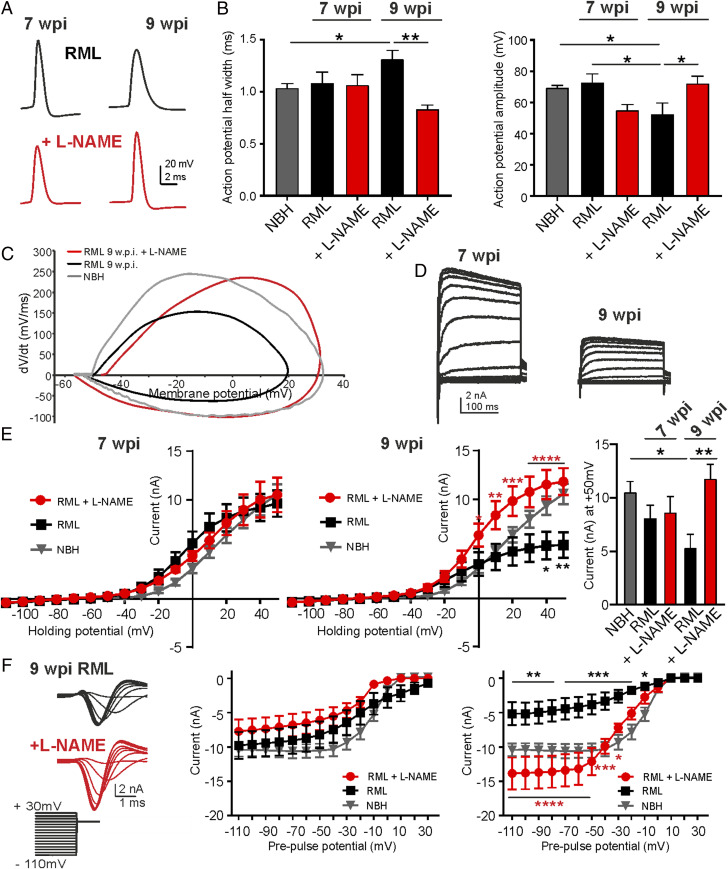
Fig. 3.
Neuronal function is protected by NOS antagonism. (A) Representative current-evoked AP recordings. (B) AP half-width and amplitudes were analyzed at 7 and 9 w.p.i. for NBH (gray), vehicle-treated (black), and L-NAME–treated RML (red) mice. (C) Phase plots for averaged APs from NBH, RML, and RML + L-NAME–treated mice. Note the strongly reduced upstroke values (dV/dt) and amplitudes in RML mice which were recovered following L-NAME treatment. (D) Representative recordings of voltage-gated potassium currents at 7 and 9 w.p.i. in RML mice. (E) IV relationships at 7 and 9 w.p.i. for NBH, RML, and RML + L-NAME–treated mice. Treatment prevented the decline in voltage-gated potassium currents at 9 w.p.i. (red). (Right) Mean currents at +50 mV. (F) Voltage-gated sodium currents decline at 9 w.p.i. in RML mice with L-NAME treatment (red) preventing the reduction in currents at 9 w.p.i. (representative recordings at 9 w.p.i.). Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 4 NBH, n = 9 RML and n = 6 RML + L-NAME–treated mice with n = 4 to 6 neurons per mouse, one-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.