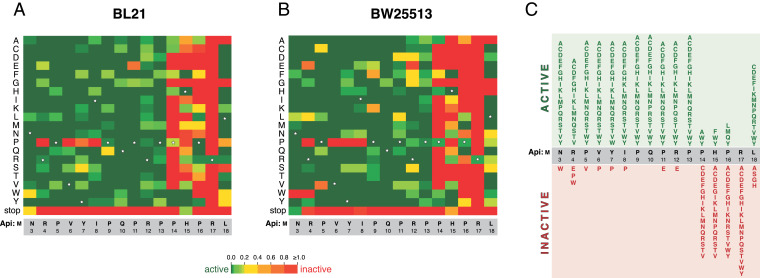
Fig. 4.
The effects of single-amino-acid substitutions on the activity of endogenously expressed Api(Δ2) in (A) BL21 or (B) BW25113 E. coli strains. The activity plots were computed as the ratio of the fraction of each mutant in the library of clones formed on inducing (arabinose) or noninducing (glucose) plates. The green rectangles indicate the mutations that preserve the activity of the PrAMP; the red rectangles show the inactivating mutations. For the intermediate effects, refer to the heatmap scale. Rectangles corresponding to the amino acid residues of the WT Api are indicated by stars. (C) Summary diagram for the effects of the mutations. A substitution was considered to render an active variant (green) when it caused reduction of the occurrence of the mutant clone on the arabinose plate by at least two-fold in at least one of the two strains tested.