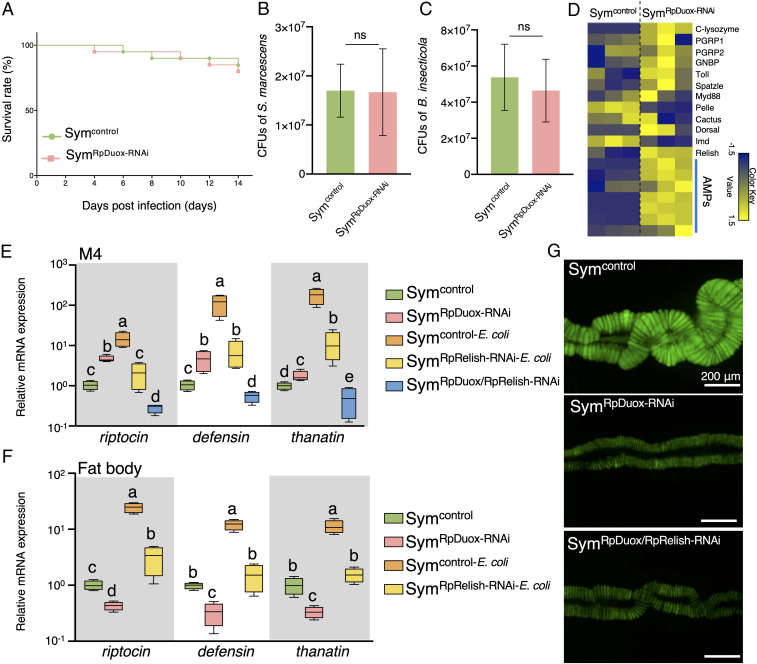
Fig. 2.
RpDuox function is not related to gut mucosal immunity in the bean bug. (A) The survival rate of Sym (Symcontrol) and RpDuox-RNAi (SymRpDuox-RNAi) insects after oral infection with 107 cells per milliliter of S. marcescens (n = 20 insects). (B) Number of S. marcescens colonies from the M3 region of third-instar nymph Symcontrol and SymRpDuox-RNAi insects. (C) The number of Burkholderia symbionts in the M3 of the third-instar nymph Symcontrol and SymRpDuox-RNAi insects. CFU, colony-forming units. (D) Expression profile from RNA sequencing data of immunity-related genes in the M4 of Symcontrol and SymRpDuox-RNAi insects. Each column is a replicate experiment. (E) The expression level of AMPs in the M4 of Sym insects without immune stimulation (Symcontrol), Symcontrol with septic injury by Escherichia coli injection in the hemolymph (Symcontrol-E. coli), RpRelish-RNAi with E. coli injection (SymRpRelish-RNAi-E.coli), RpDuox-RNAi without bacterial injection (SymRpDuox-RNAi), and double RpDuox/RpRelish-RNAi insects without bacterial injection (SymRpDuox/RpRelish-RNAi). (F) The expression level of AMPs in the fat body. Data shown in B and C are from n = 5 insects, and those in E and F are from n = 4 insects. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences (P < 0.05). The statistical significance was analyzed by the Mann–Whitney U test (B and C) or Kruskal–Wallis test with Bonferroni correction (E and F). Error bars indicate SDs; ns, not statistically significant. (G) Effect of RpDuox/RpRelish double RNAi on symbiosis. Green color indicates the GFP signal from gut-colonizing Burkholderia symbionts.