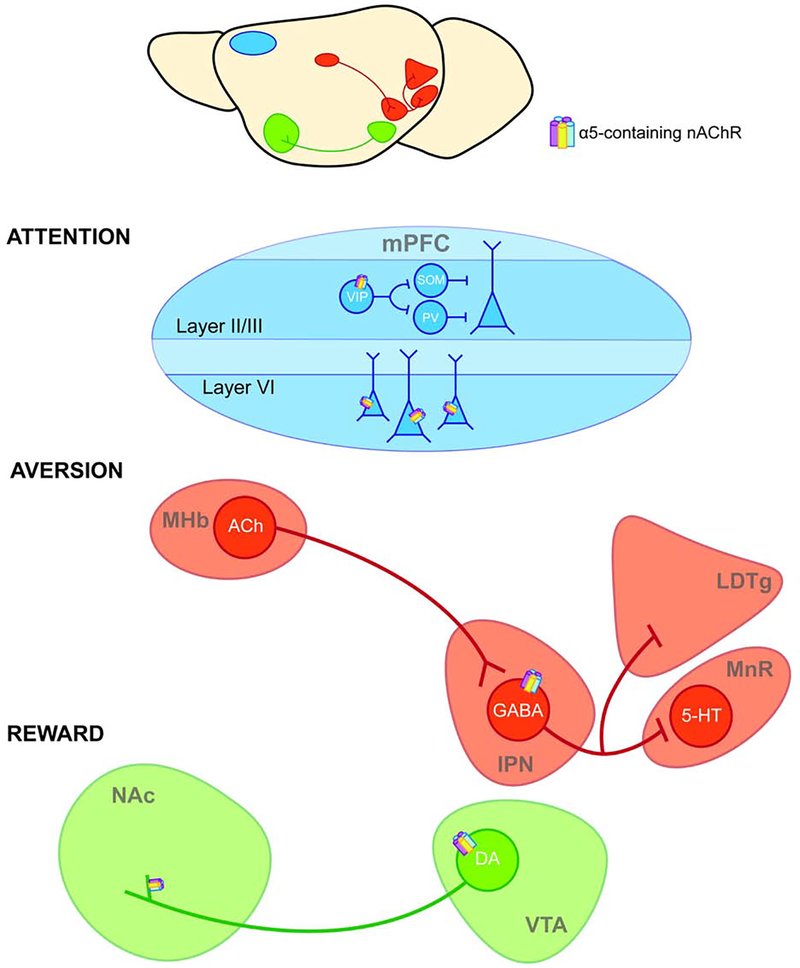
Figure 1. CHRNA5 D398N alters the function of α5 nAChR subunits within addiction-relevant circuitry.
CHRNA5 D398N impacts the function α5 nAChR subunits that are expressed within neural circuits implicated in attention (mPFC), aversion (MHb-IPN), and reward (VTA-NAc). In layer II/III of the mPFC, α5-containing nAChRs are expressed on vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) interneurons that inhibit somatostatin- (SOM) and parvalbumin- (PV) interneurons; these interneurons inhibit pyramidal cells (Pi et al., 2013). In layer VI, α5-containing nAChRs are expressed on pyramidal neurons (Bailey et al., 2012). α5 subunits are also located on GABAergic neurons in the IPN, where they mediate aversion via inhibitory projections to the mesopontine raphe (MnR) and laterodorsal tegmental area (LDTg) (Hsu et al., 2013; Morton et al., 2018; Quina et al., 2017; Wolfman et al., 2018), and on the cell bodies and terminals of DA neurons that project from the VTA to the NAc (Salminen et al., 2004; Zoli et al., 2002), where they mediate reward.