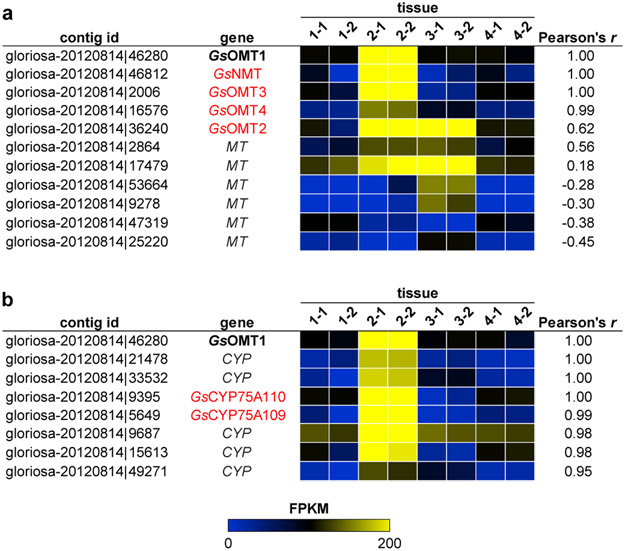
Figure 2. Candidate methyltransferase (MT) and cytochrome P450 (CYP) transcripts identified within the public Gloriosa superba transcriptome via expression correlation analysis.
Discovery of a tentative function for GsOMT1 within colchicine alkaloid biosynthesis prompted its use as a query for Pearson correlation analysis of contig expression within the public G. superba transcriptome (87,123 contigs compared across 8 tissue samples). The expression of each candidate transcript is represented as the fragments per kilobase of trascript per million mapped reads (FPKM). Tissue samples 1 thru 4 represent distinct tissue types with two replicate libraries of each. a) Comparison of GsOMT1 expression to previously cloned MT candidate gene transcripts. b) Identification of CYP transcripts that show strong co-expression with GsOMT1. Candidate genes ultimately found to have a role in colchicine alkaloid biosynthesis are highlighted in red.