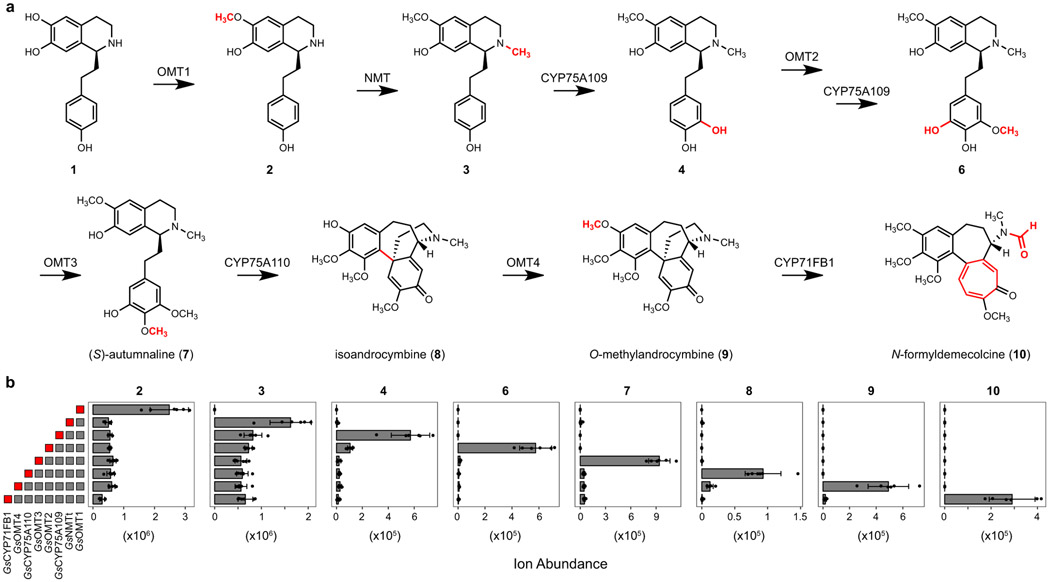
Figure 4. Discovery of a pathway for colchicine alkaloid biosynthesis.
Transient co-expression of eight identified biosynthetic genes from G. superba within N. benthamiana allows for step-by-step conversion of a co-infiltrated 1-phenethylisoquinoline substrate (1) into the tropolone-containing alkaloid N-formyldemecolcine (10) via the proposed pathway shown here. Gray boxes to the left of the bar graphs indicate biosynthetic genes included within a co-expression experiment, with the red box indicating the final acting enzyme within a set of co-expressed genes. Shown for each intermediate is the mean extracted ion abundance (n=6, ± standard deviation) for the exact ion mass [M+H]+ (for 10, both [M+H]+ and [M+Na]+) that corresponds to each compound.