Fig. 3 |. Isolating stimulus-locked brain connectivity using inter-subject functional correlation.
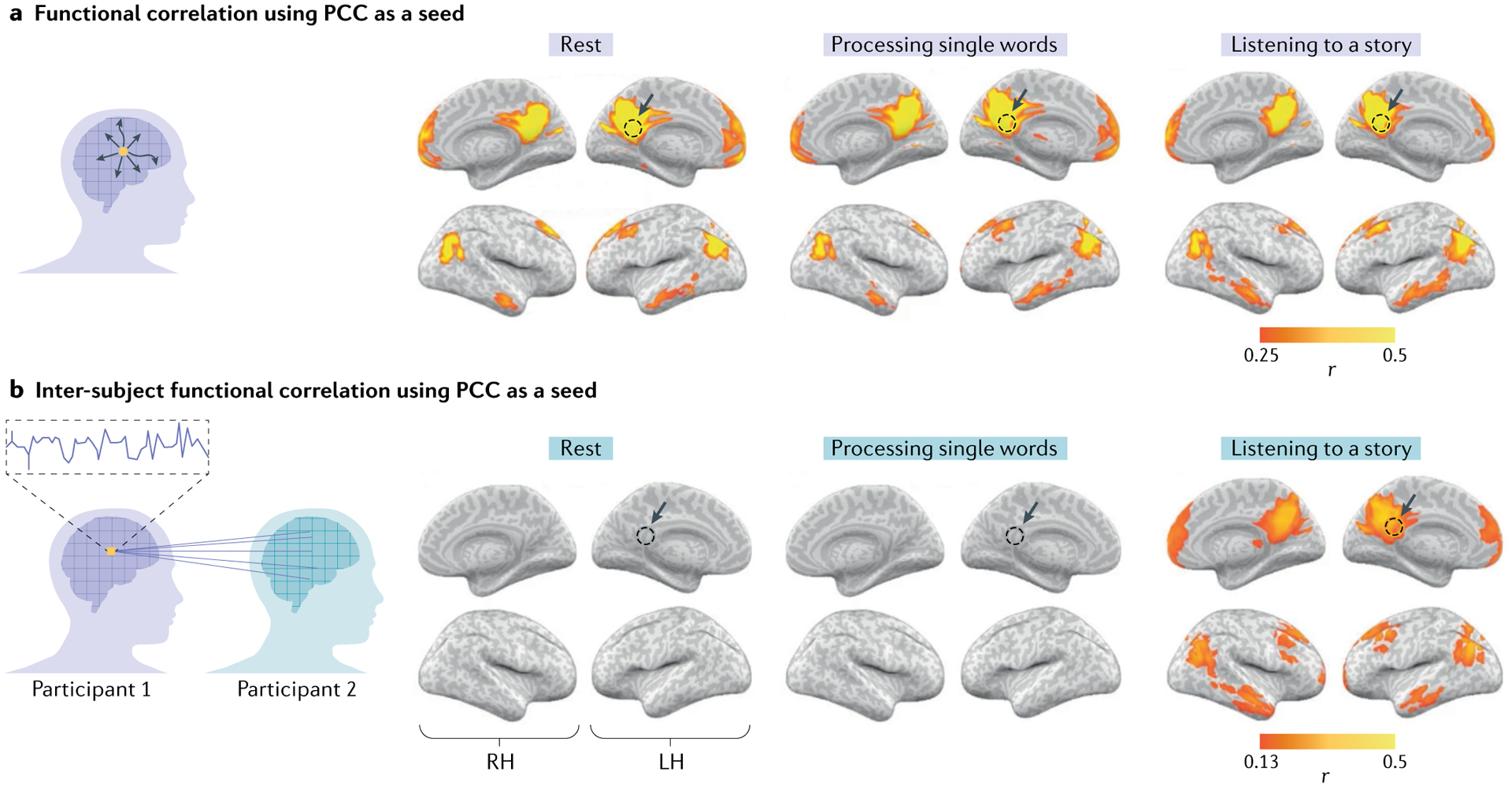
a | Within-participant functional correlation maps between the posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) seed (yellow voxel in the schematic; dashed circles in the brain maps) and the whole-brain neural activity. The functional correlation analysis delineates nodes of the default mode network (DMN) in which the activity fluctuates together (co-varies) in a given participant, owing to the direct or indirect anatomical connections during rest (left panel), processing of single words (middle panel) and listening to a coherent story (right panel). b | Inter-subject functional correlation maps between the PCC seed and the whole-brain neural activity observed in other participants. This analysis can filter out spontaneous intrinsic neural facilitation, and as such reveals no substantial stimulus-locked correlations in the DMN during rest (left panel) or during the processing of single words (middle panel). By contrast, however, inter-subject functional correlation exposed stimulus-locked shared responses across participants in the DMN as subjects listen to and process a spoken story minutes long (right panel). LH, left hemisphere; RH, right hemisphere. Adapted from REF.26, CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
