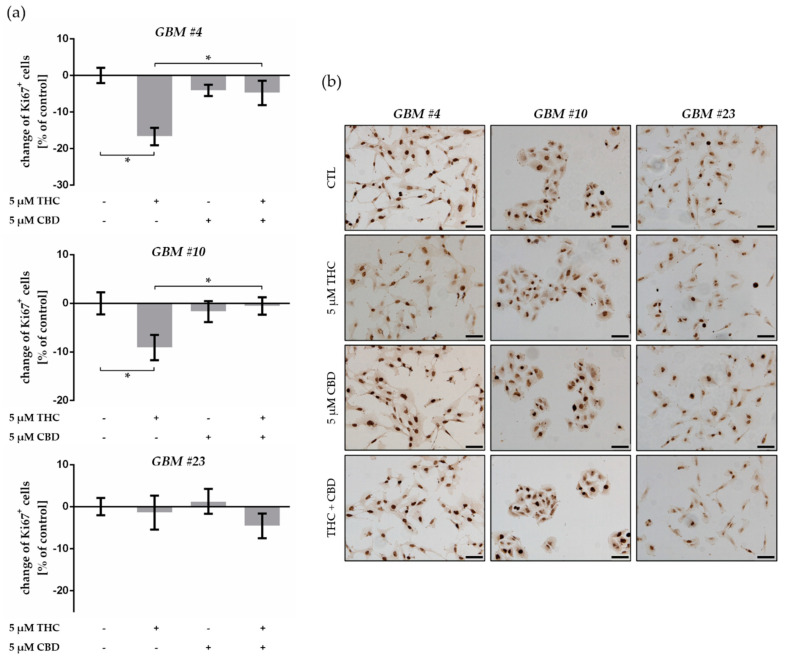
Figure 2.
Impact of ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) on proliferation capacity of human patient-derived GBM cells. (a) Effects of THC and CBD on the number of Ki67-labelled GBM cells. In comparison to control group, application of THC (5 µM) for 24 h produced a significant reduced number of Ki67+ cells in GBM #4 and GBM #10, but not in GBM #23. Alterations after treatment with CBD (5 µM) were not observed, but in combination with THC it reversed the effects of THC in GBM #4 and GBM #10. Data are means ± SEM of N = 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. Significance was chosen for p < 0.05. The asterisk denotes significant results regarding the respective measurement indicated with the bar. (b) Representative images of Ki67-immunoreactive GBM cells (Ki67+ in brown and Ki67- in blue) untreated (CTL) or treated with THC (5 µM), CBD (5 µM), and an equimolar combination of THC and CBD after 24 h. Nuclei were counterstained using hematoxylin. Scale bar = 75 µm.