Figure 8. Performance in the context fear discrimination task is improved in rmCHI Sarm1−/− mice.
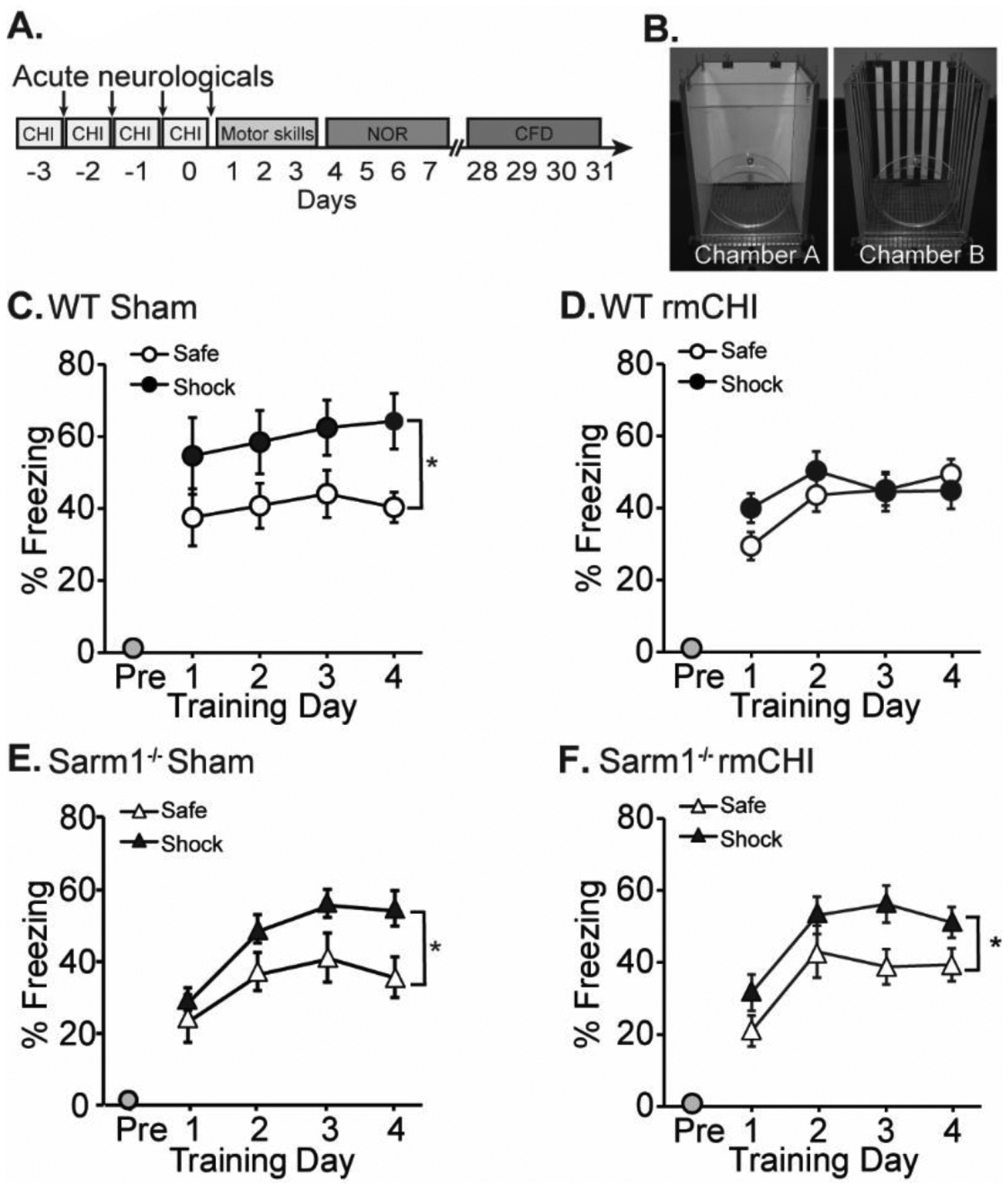
(A) Timeline of injury and cognitive assessments. Context fear discrimination was tested four weeks after the last injury. (B) Mice are trained to differentiate between “Shock” and “Safe” chambers that share some features, but differ in others. (C) Wild-type sham mice freeze more in the “shock” chamber versus the safe chamber. (D) Wild-type rmCHI mice are impaired in their ability to discriminate between the two contexts, as indicated by similar freezing behavior in both chambers. (E) Sham Sarm1−/− mice and (F) rmCHI Sarm1−/− mice are able to discriminate between the two contexts. *significant difference between freezing in “safe” and “shock” context. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05.
