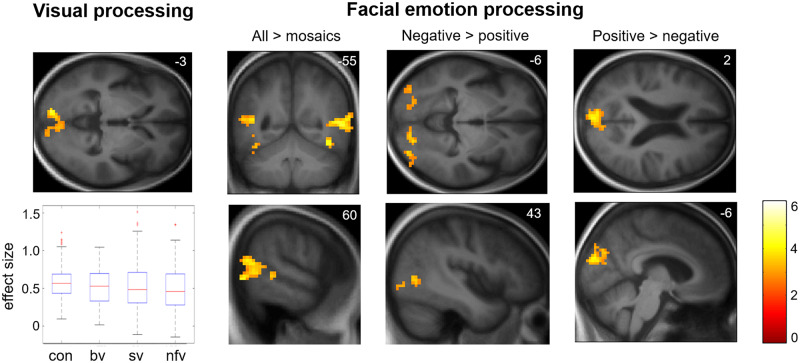
Figure 1.
Functional neuroanatomy of facial emotion viewing: effect of condition. Statistical parametric maps (SPMs) of T contrasts for effect of condition across all participants for early visual processing (visual stimulus > fixation cross contrast; left) and facial emotion processing (contrasts for all facial expressions > dynamic mosaic baseline, positive facial expressions > negative expressions, negative facial expressions > positive expressions) together with a plot (bottom left) of effect sizes (beta-values) demonstrating consistent activation of bilateral primary visual cortex across participant groups (box and whisker plots display median, interquartile range, minimum and maximum values, with outliers appearing as red crosses). SPMs are thresholded at the cluster-defining threshold of P < 0.005 uncorrected and displayed on sections of the structural group mean T1-weighted template brain image. The plane of each section (in mm in MNI space) is shown in the top right of each image; axial sections show the left hemisphere on the top and the coronal section shows the left hemisphere on the left. The colour bar codes T-values (the same range applies to SPMs in other figures, unless otherwise indicated). bv = patient group with bvFTD; con = healthy control group; nfv = patient group with nfvPPA; sv = patient group with svPPA.