Fig 1. Effect of Campylobacter jejuni challenge on Campylobacter colonization kinetics in the ceca, spleen, and liver.
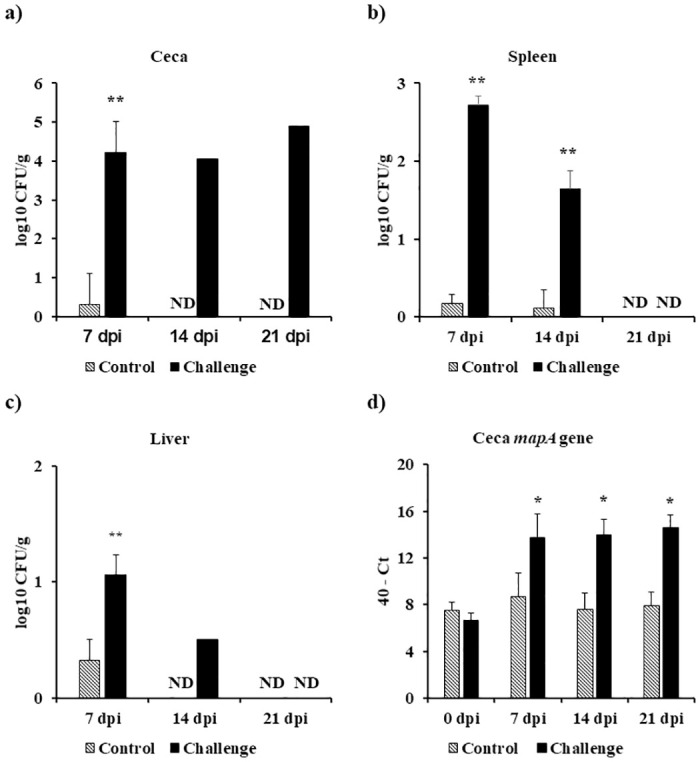
On d14 of age, birds were weight-matched and randomly assigned to two treatments: control and challenge. Birds were orally challenged with 0.5 mL of 2.4 x 108 CFU/mL of Campylobacter jejuni or mock-challenged with 0.5 mL of 0.85% saline. Colonization of the (a) Ceca, (b) Spleen, and (c) Liver was estimated by micro-dilutions method (CFU/g) and then log transformed to log10 CFU/g for statistical analysis. (d) Campylobacter jejuni in the ceca was quantified using SyBr green qPCR with primers targeting C. jejuni mapA gene. Transcript levels were reported as 40—Ct for statistical analysis. Results were expressed as mean + SEM. Non-detectable (ND). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 compared with control (n = 6), Student’s t-test.
