FIG 3.
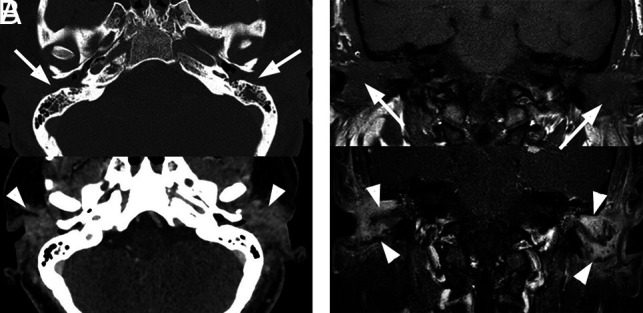
Bilateral external otitis. A 44-year-old woman presented with severe bilateral ear pain and drainage with conductive hearing loss. Clinically, there was marked inflammatory thickening of the EACs bilaterally. Pseudomonas species were cultured from the external auditory canals bilaterally. The patient was treated with IV vancomycin and piperacillin/tazobactam for 4 days followed by 2 weeks of oral ciprofloxacin. Symptoms resolved at 3 weeks without additional imaging work-up. A, Axial enhanced CT images are shown. Upper image with bone windows shows marked opacification of the EACs (arrows). The lower image with a soft-tissue filter shows marked inflammation of the EACs and periauricular tissues (arrowheads). B, The upper coronal T1 image shows marked opacification and thickening of the EACs (arrows) and associated opacification of the middle ear cavities. The lower image depicts postcontrast fat-saturated T1 images. A discrete mass is not identified. However, there is marked enhancement along the walls of the EACs (arrowheads), compatible with otitis externa.
