FIG 4.
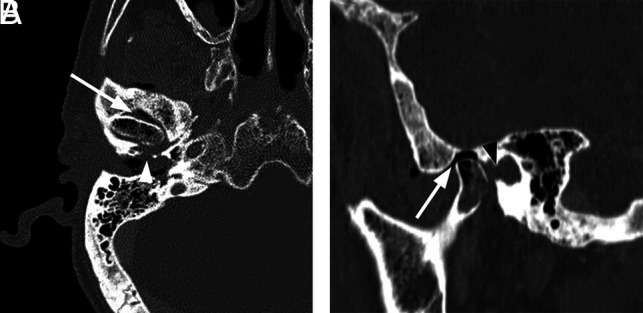
Necrotizing external otitis complicated by septic temporomandibular joint arthritis. An 88-year-old man with several months of right ear pain and drainage presented with progressive symptoms and right temporomandibular joint pain and trismus. In the prior weeks, he had been treated for NEO with oral and IV antibiotics at an outside facility. After initial evaluation, debridement and temporomandibular joint replacement were planned, but the patient was lost to follow-up. A, Axial contrast-enhanced CT with bone windows demonstrates abnormal opacification of the right EAC and inferior middle air cavity. There is erosion of the floor of the EAC, potentially involving the foramen of Huschke (arrowhead), and communication with the right temporomandibular joint. Air/gas density is identified within the temporomandibular joint (arrow) as well as within the mandibular condyle itself. B, Sagittal reformatted CT scan again demonstrates abnormal air density within the right temporomandibular joint and mandibular condyle (arrow). Note a defect in the anterior inferior margin of the EAC (black arrowhead).
