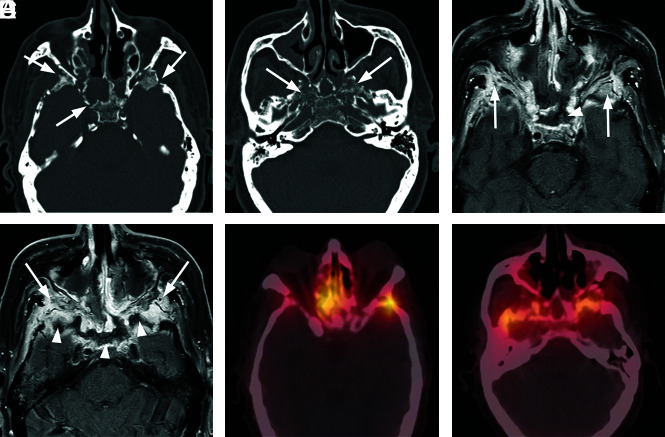
FIG 6.
Extensive atypical skull base osteomyelitis secondary to invasive fungal sinusitis (mucormycosis). A 68-year-old man with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and a history of chronic sinusitis and previous sinus operations presented with a 6-month history of severe headache, nausea and vomiting, and weight loss. Endoscopic debridement and biopsies were performed. While cultures were negative for fungus, pathologic evaluation of sinus material yielded microscopic evidence of invasive fungal sinusitis consistent with mucormycosis. The patient was treated with micafungin and amphotericin B. A protracted course was complicated by persistent symptoms, and the patient had additional sinonasal debridement at 4 months. Endoscopic culture at that time yielded P aeruginosa as a new or potentially coexistent organism, and IV ceftazidime was added to treatment. The patient was followed clinically and with CT/MR imaging until resolution. A, Axial unenhanced CT image through the skull base demonstrates diffuse osteolysis and fragmentation of the sphenoid bone, including the walls of the sphenoid sinus and greater wing (arrows). There is marked mucosal thickening and opacification of the visualized sinuses. B, Axial CT image through the central skull base shows diffuse bone demineralization of the body of the sphenoid bone (arrows). C, Axial T1-weighted fat-saturated contrast-enhanced image shows abnormal enhancement in the greater wings of the sphenoid bone bilaterally (arrows) and confluent opacification of the sinuses. There is evidence of devitalization and necrosis in the upper clivus (arrowhead). D, Axial T1-weighted fat-saturated contrast-enhanced image shows marked infiltrative signal abnormality and enhancement in the greater wings of the sphenoid bone (arrows). There is marrow necrosis and devitalization of the body of the sphenoid bone centrally (arrowheads). E, Axial fused Tc99m MDP bone scan SPECT image shows marked radiotracer uptake in the greater wing of the sphenoid bone on the left and the anterior midline skull base, consistent with osteomyelitis. F, Axial fused Tc99m MDP bone scan SPECT image shows multifocal areas of radiotracer uptake in the sphenoid bone bilaterally.