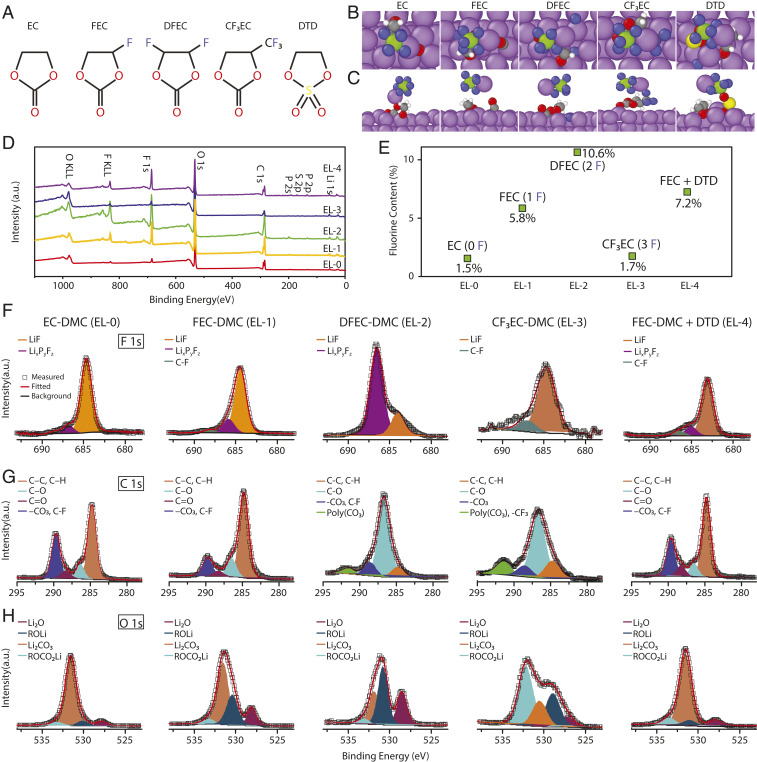
Fig. 2.
Decomposition of selected molecules at the Li surface studied by DFT calculations and XPS. (A) Molecular structure of EC, FEC, DFEC, CF3EC, and DTD. B and C are top and side views, respectively, of final decomposition products of EC, FEC, DFEC, CF3EC, and DTD at Li (100) surface in the presence of LiPF6, as predicted by DFT calculations. The purple atoms represent Li, red represent O, gray represent C, green represent P, blue represent F, yellow represent S, and silver represent H. FEC and DTD break down completely, while DFEC decomposes partially and CF3EC does not undergo significant breakdown. DTD also catalyzes the decomposition of LiPF6, leading to formation of LiF. (D) Wide-scan XPS spectra collected from the surface of the Li film deposited in 1 M LiPF6 EC-DMC (EL-0), 1 M LiPF6 FEC-DMC (EL-1), 1 M LiPF6 DFEC-DMC (EL-2), 1 M LiPF6 CF3EC-DMC (EL-3), and 1 M LiPF6 FEC-DMC + DTD (EL-4). (E) F content at the surface of the Li film deposited in different electrolytes. F content increases in the order of EL-3, EL-0, EL-1, EL-4, and EL-2. F–H are narrow-scan XPS spectra of F 1s, C 1s, and O 1s, showing that DFEC and CF3EC decompose differently from FEC, despite their structural similarity. a.u., arbitrary units.