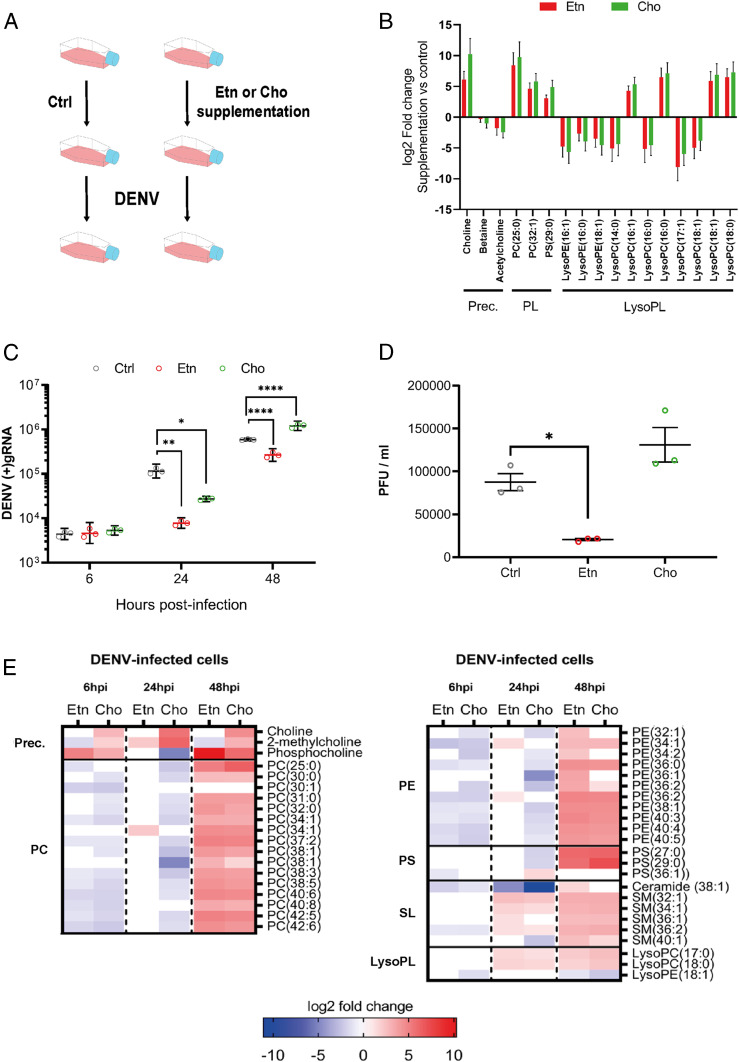
Fig. 2.
Impact of de novo PL production on DENV and phospholipid reconfiguration. Aag2 cells were supplemented with 2 mM of either Etn or Cho for 24 h before and throughout infection with DENV at a MOI of 1. (A) Experimental design. (B) Impact of the supplementations on the phospholipidome before infection. Fold changes of only significantly regulated metabolites (|log2 fold change| > 1 and P < 0.05) with a lipid or precursor (Prec.) annotation compared to control media are shown. Lines indicate means ± SEM from three biological repeats. (C) Impact of the supplementations on DENV (+)gRNA at 6, 24, and 48 hpi. Lines show geometric means ± 95% CI from three biological repeats. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001, as determined by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. (D) Impact of the supplementations on infectious particle production as determined by PFUs. Lines show mean ± SEM from three biological repeats. *P < 0.05, as determined by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. (E) Impact of the supplementations on the phospholipidome at 6, 24, and 48 hpi. Fold changes of significantly regulated metabolites (|log2 fold change| > 1 and P < 0.05) compared to media control within the same time point for three biological replicates are shown. SL, sphingolipid.