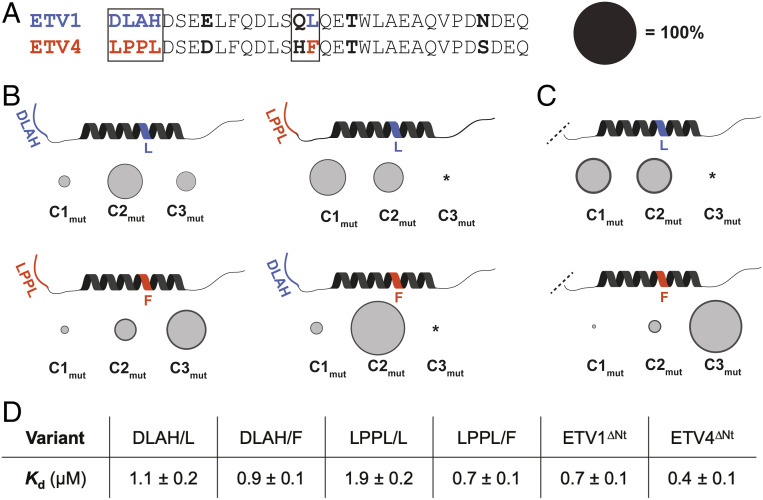
Fig. 3.
Variable residues in the disordered N terminus and the helical binding region mediate differences in ETV/PEA3•Med25 conformational behavior. (A) Alignment of ETV1 and ETV4 activators with regions that were selected for mutational analysis boxed. Bolded residues are conserved between ETV1 and ETV5, but not ETV4. Regions/residues that affected the conformational ensemble are color coded to ETV1 (blue) or ETV4 (orange). Effects of the Gln/His residues in the variable motif were also tested but did not affect conformational populations and are thus omitted in B and C for clarity. Populations of conformational states in B and C are scaled relative to the diameter of the black circle. (B) Results from kinetics experiments of mutant TADs, for native (Left) and nonnative (Right) combinations of variable N termini and helical binding regions. Variants were made based on the ETV4 sequence. The data shown are the average across all of the variants tested from each group, with the error (dark gray outer circle) representing the SD. (C) Results from kinetics experiments with ETV1∆Nt (Top) and ETV4∆Nt (Bottom). (D) Average equilibrium Kd values of variants tested. *Conformer was undetectable in kinetics experiments (see SI Appendix, Discussion of Kinetic Data Analysis for further details).