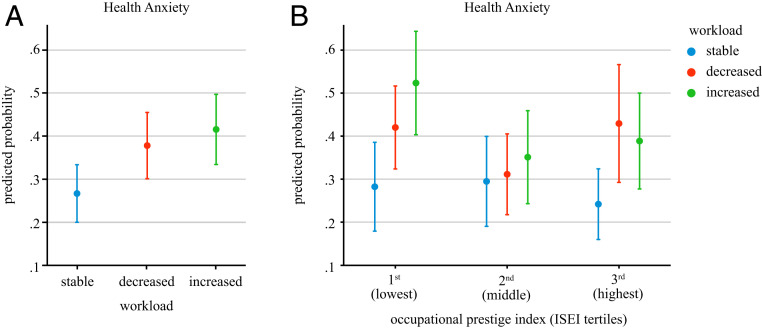
Fig. 5.
Predicted probabilities of workload change during COVID-19 affecting health anxiety. (A) Marginal effect of workload change on feelings of depression. (B) Marginal effect of workload change on feelings of depression by ISEI level. Marginal effects are drawn from logit regressions with country-random intercepts. Estimates are adjusted for age, age squared, gender, migration background, partner (in household), employment status, firm size, urbanicity, and timing/survey week number. Interval bars represent 95% CIs (two-tailed tests).