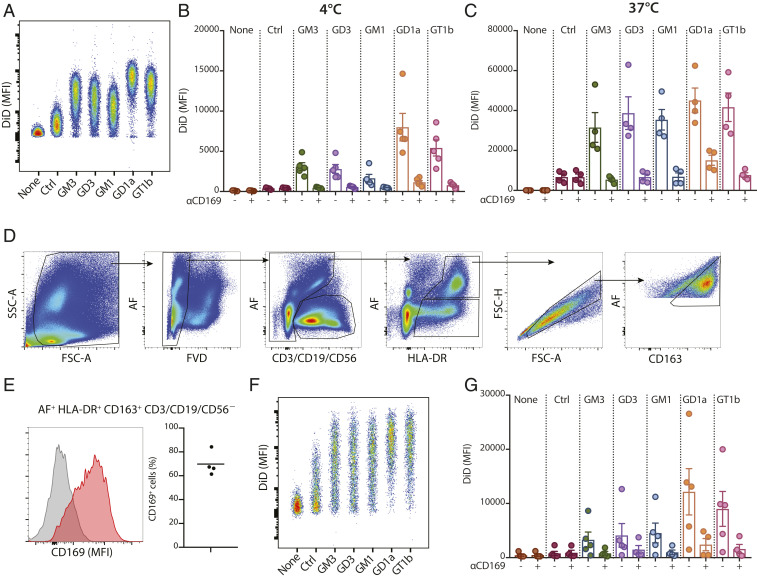
Fig. 2.
Ganglioside-liposomes bind CD169-expressing moMacs and human splenic macrophages. (A and B) DiD-labeled ganglioside-liposomes were incubated with moMacs, and binding (4 °C; A and B) and uptake (37 °C; C) was determined by flow cytometry. Data are mean ± SEM from four independent donors. (D) Human spleen cells were incubated with ganglioside-liposomes at 37 °C for 45 min and stained for cell lineage markers. Gating strategy of autofluorescence+ (AF) HLA-DR+ CD163+ CD3/CD19/CD56− macrophages is displayed. (E) The expression of CD169 on human splenic macrophages is shown as a representative histogram (Left; gray, fluorescence minus one; red, CD169) and percentages (Right; n = 4). (F and G) Ganglioside-liposome uptake by human splenic macrophages as (F) representative dot plot and (G) quantification (n = 4 to 5) is shown. When indicated, macrophages were preincubated with anti-CD169 blocking antibody to block ganglioside-liposome binding. Data are mean ± SEM from n = 4 to 5 donors.