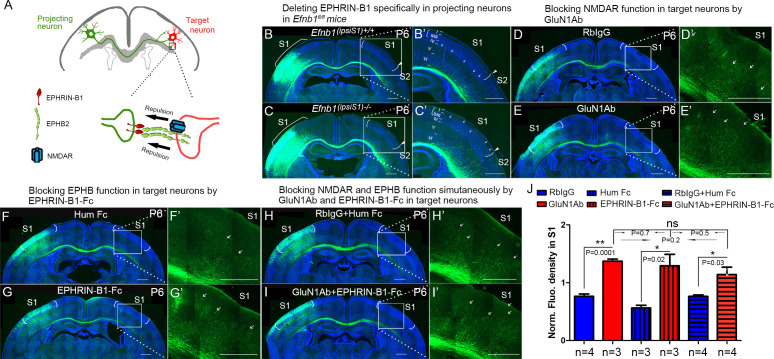
Figure 8. NMDARs cooperate with EPHRIN-B/EPHB in controlling axon targeting in S1.
(A) EPHRIN-B1, expressed by the projecting neuronal axons, signals through EPHB2 and NMDAR, located on the target neurons, regulates axon extension in contralateral cortex. (B, C) Deleting EPHRIN-B1 in projecting neurons in Efnb1fl/fl mice. Vectors expressing Cre and EGFP were delivered into S1 of all pups from Efnb1fl/wt × Efnb1fl/wt crosses by in utero electroporation at E15.5. Compared with control mice (B), ipsilaterally deleted mice showed earlier callosal innervation at P6 (C). (D, E) Blocking NMDAR function in target neurons by intraventricular injection of GluN1Ab in contralateral cortex, from P3 to P6. Compared with control RbIgG injected mice (D), GluN1Ab injected mice showed earlier callosal innervation at P6 (E). (F, G) Blocking EPHB function in target neurons by intraventricular injection of EPHRIN-B1-Fc in contralateral cortex, from P3 to P6. Compared with control Hum Fc injected mice, EPHRIN-B1-Fc injected mice showed earlier callosal innervation at P6 (G). (H, I) Blocking NMDAR and EPHB function simultaneously by GluN1Ab and EPHRIN-B1-Fc in contralateral cortex, from P3 to P6. Compared with control RbIgG + Hum IgG injected mice (H), GluN1Ab + EPHRIN-B1-Fc injected mice showed earlier callosal innervation at P6 (I). (J) Quantification of fluorescence density. Scale bar: 500 μm for all images. Arrows pointed out axon terminals in the target cortex.